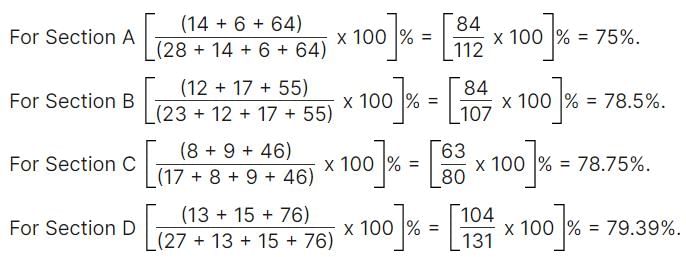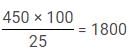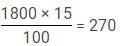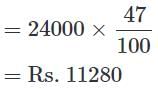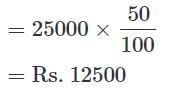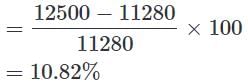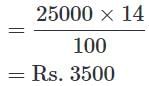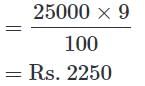SSC CGL (Tier II) Practice Test - 20 - SSC CGL MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SSC CGL (Tier II) Practice Test - 20
A school has four sections A, B, C, D of Class IX students.
The results of half yearly and annual examinations are shown in the table given below.
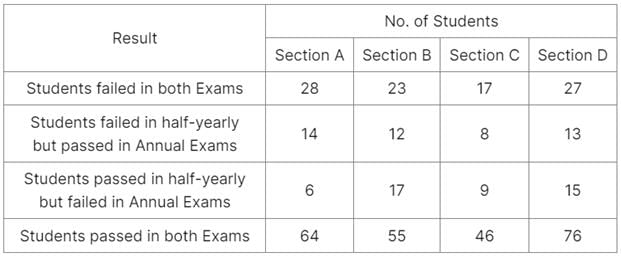
Q. How many students are there in Class IX in the school?

A school has four sections A, B, C, D of Class IX students.
The results of half yearly and annual examinations are shown in the table given below.
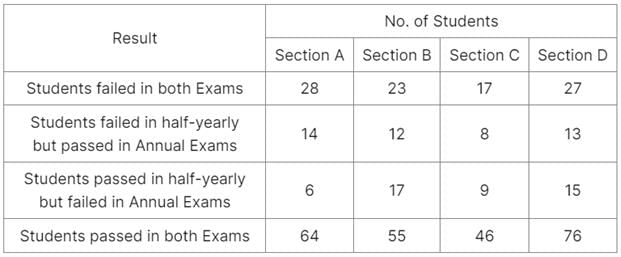
Q. Which section has the maximum pass percentage in at least one of the two examinations?

Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
The following graph shows the percentage break-up of sales of units of different products in 2018.

Product A is sold at Rs.40/unit. The shopkeeper earns Rs.18000 from product A.
Q. The shopkeeper made Rs. 25 profit on each unit of product B. How much profit did the shopkeeper make?
The following graph shows the percentage break-up of sales of units of different products in 2018.

Product A is sold at Rs.40/unit. The shopkeeper earns Rs.18000 from product A.
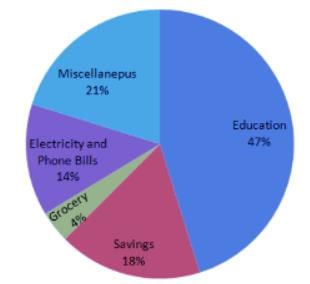
Directions: In the following question, study the two pie-charts and answer the questions.
April Month's Salary = Rs. 24000.
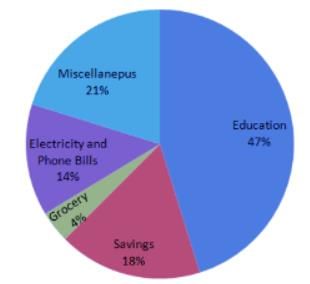
May Month's Salary = Rs. 25000.
Q. What is the percent increase in Education in May month than April month?
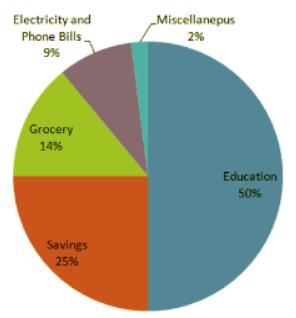
Directions: In the following question, study the two pie-charts and answer the questions.
April Month's Salary = Rs. 24000.
May Month's Salary = Rs. 25000.
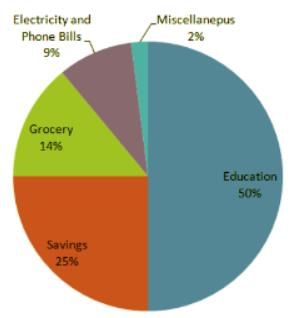
Q. From the salary of May, the amount spent on Grocery and Electricity are:
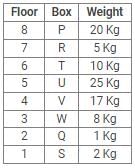
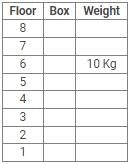
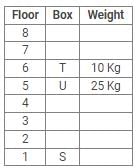
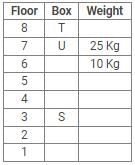
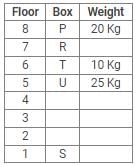
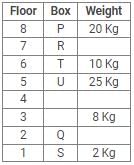
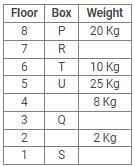
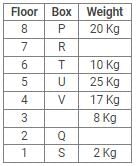
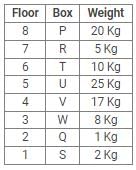
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Eight boxes – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W were placed in an almirah of eight shelves. The bottom shelf was numbered 1 and the topmost shelf was numbered 8. Each of these boxes contained different amount of Sugar – 25 kg, 20 kg, 17 kg, 10 kg, 8 kg, 5 kg, 2 kg and 1 kg but not necessarily in the same order.
Box V was placed at one of the even numbered shelves and contained 17 kg of Sugar. The box which was placed on 6th shelf contained 10 kg of Sugar. Box Q was placed immediately below the box which contained 8 kg of Sugar and immediately above the box which contained 2 kg of Sugar. Box R was not the lightest and Box U, was the heaviest. Box R was placed above the shelf on which Box U was placed but not on the even numbered shelf. Box P, contained 20 kg of Sugar, and was placed either at the top or bottom shelf. There are three boxes between Box U and Box S and Box S was placed below the shelf on which Box U was placed. T was placed immediately above the box which was heaviest.
Q. What amount of Sugar was contained by Box Q?
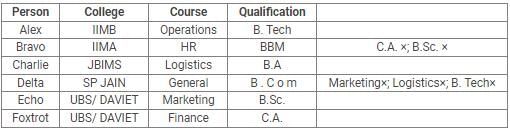
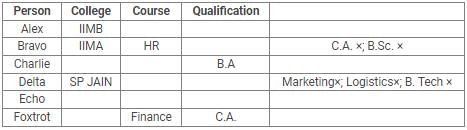
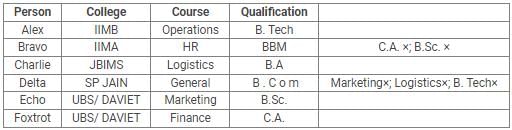
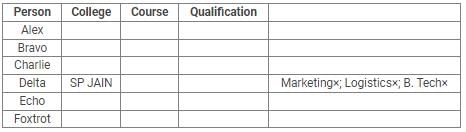
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
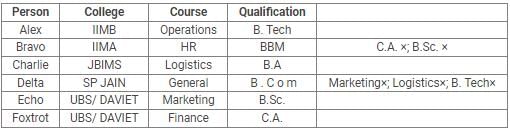
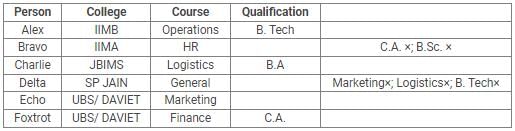
Alex, Bravo, Charlie, Delta, Echo and Foxtrot joined six different colleges – UBS, SP JAIN, DAVIET, JBIMS, IIMA and IIMB and opted for six different courses in management – Marketing, Finance, Operations, HR, Logistics and General Management.
Each of them has a different educational qualification out of B. Tech, B.Sc, B.Com, C.A, BBM and BA.
The following information is available about them:
- Delta joined SP JAIN and did not take up Marketing or Logistics and is not a B. Tech.
- The person who joined IIMA opted for HR and is not a C.A or B.Sc.
- Foxtrot is a C.A and has taken Finance management.
- The person, who is a B.A graduate, joined JBIMS and took Logistics. Whereas, the person, who is a B.Com graduate, took up General Management.
- The person, who is a B. Tech graduate, has taken Operations Management and did not join UBS or DAVIET.
- Alex joined IIMB, Charlie is B.A graduate and Bravo took up HR.
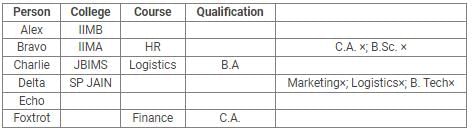
Q. Which courses did Charlie opt for in his MBA?
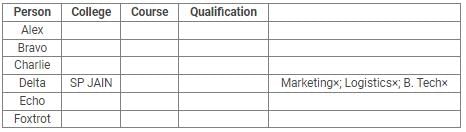
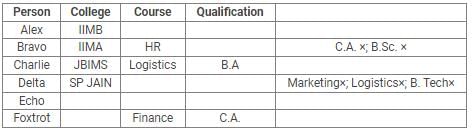
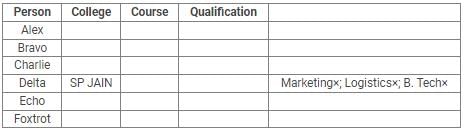
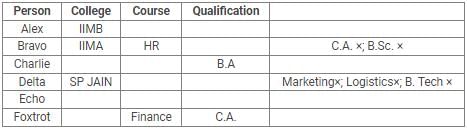
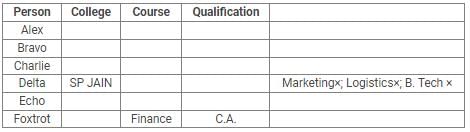
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Alex, Bravo, Charlie, Delta, Echo and Foxtrot joined six different colleges – UBS, SP JAIN, DAVIET, JBIMS, IIMA and IIMB and opted for six different courses in management – Marketing, Finance, Operations, HR, Logistics and General Management.
Each of them has a different educational qualification out of B. Tech, B.Sc, B.Com, C.A, BBM and BA.
The following information is available about them:
- Delta joined SP JAIN and did not take up Marketing or Logistics and is not a B. Tech.
- The person who joined IIMA opted for HR and is not a C.A or B.Sc.
- Foxtrot is a C.A and has taken Finance management.
- The person, who is a B.A graduate, joined JBIMS and took Logistics. Whereas, the person, who is a B.Com graduate, took up General Management.
- The person, who is a B. Tech graduate, has taken Operations Management and did not join UBS or DAVIET.
- Alex joined IIMB, Charlie is B.A graduate and Bravo took up HR.
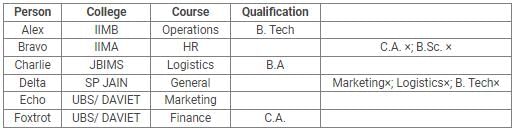
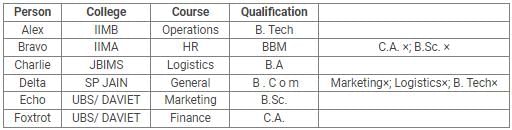
Q. What is the educational qualification of Delta and what is the course he opted for?
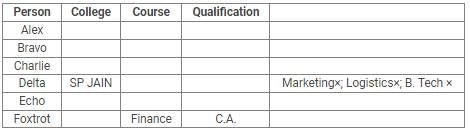
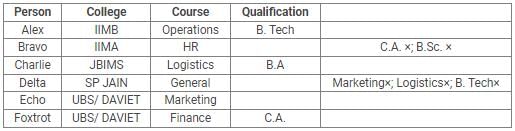
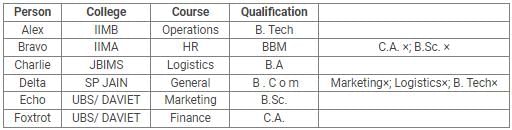
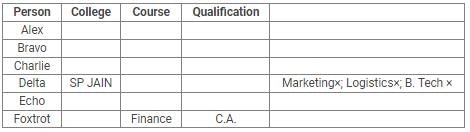
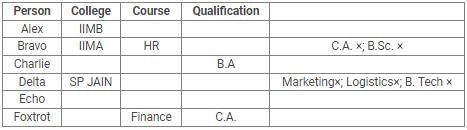
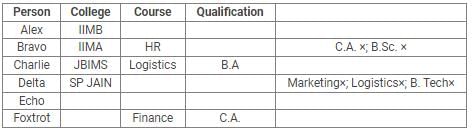
Directions: Read the following information carefully and answer the questions.
Alex, Bravo, Charlie, Delta, Echo and Foxtrot joined six different colleges – UBS, SP JAIN, DAVIET, JBIMS, IIMA and IIMB and opted for six different courses in management – Marketing, Finance, Operations, HR, Logistics and General Management.
Each of them has a different educational qualification out of B. Tech, B.Sc, B.Com, C.A, BBM and BA.
The following information is available about them:
- Delta joined SP JAIN and did not take up Marketing or Logistics and is not a B. Tech.
- The person who joined IIMA opted for HR and is not a C.A or B.Sc.
- Foxtrot is a C.A and has taken Finance management.
- The person, who is a B.A graduate, joined JBIMS and took Logistics. Whereas, the person, who is a B.Com graduate, took up General Management.
- The person, who is a B. Tech graduate, has taken Operations Management and did not join UBS or DAVIET.
- Alex joined IIMB, Charlie is B.A graduate and Bravo took up HR.
Q. If Echo joined DAVIET, then the student who joined UBS, opted for:
Directions: A number arrangement machine when given an input line of numbers rearranges them following a particular rule in each step. The following is an illustration of input and rearrangement.
Input: 62 97 38 74 55 12 86 45 68 22
Step 1: 13 62 97 38 74 55 86 45 68 23
Step 2: 39 13 62 97 74 55 86 68 23 46
Step3: 56 39 13 97 74 86 68 23 46 63
Step 4: 69 56 39 13 97 86 23 46 63 75
Step 5: 87 69 56 39 13 23 45 63 75 98
Find the different steps of output using the above-mentioned logic for the following input.
Input: 88 59 28 94 37 75 15 64 71 48
Q. How many numbers are there between 72 and the one which 4th to left of 76 in step 5?
Directions: In the following question, five statements are provided. These statements form a coherent paragraph when properly arranged. Select the alternative representing the proper and logical sequencing of these statements in the question.
1. But, equally, the benefits of reservation have not been distributed equitably.
2. There are inequalities and then there are inequalities within unequal entities.
3. The relatively rich and dominant sections among the backward castes have tended to take up a disproportionately larger share of the reservation pie.
4. Moreover, large segments of the weaker sections and backward classes continue to have no access to quality education or meaningful employment.
5. That reservation in jobs and education did address socio-economic disparities in India to some degree is true.
Direction: In each of the questions given below, a paragraph is given which has some blanks and those blanks have to be filled with the same word out of five words given below it. You have to choose that same word as your answer and fill up the blanks with that appropriate word.
His concern for the affected children is so ____________ that it can be understood without giving much thought. It is not his fault though because all his family members are ____________ in all their dealings and they do not care much about anything in life. It is because of this ____________ nature of his family that they have not got many friends in the neighbourhood.
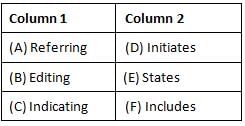
Direction: In the questions given below a sentence is given with two blanks in each. Corresponding to each question two columns are given with three words in each column. Which combination of words from the two columns will perfectly fit into the blanks to make the sentence contextually correct and meaningful?
Acute encephalitis syndrome or AES is a basket term used for ______________ to various symptoms in children with clinical neurological manifestation that ______________ mental confusion, disorientation, convulsion, delirium, or coma.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
More than three lakh workers will be employed in the solar and wind energy sectors to meet the country’s target of generating 175 gigawatts of electricity from renewable sources by 2022, an International Labour Organization (ILO) report said. The report titled, World Employment and Social Outlook (WESO) 2018: Greening with Jobs, quoted from a study conducted by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) and the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), on the changes in sectoral employment that will occur in order to meet India’s target. The study was based on surveys of solar and wind companies, developers and manufacturers.
“India is rapidly increasing its share of renewable energy sources, but still relies on coal, oil, natural gas, and the related carbon emissions for 80% of its electricity,” the report released on Tuesday said. This formed a small part of the report, which focused on the trajectory of the labour market in the backdrop of environmentally sustainable production practices. Tackling the misconception that green economies pave the way for economically undesirable outcomes, the report said rather than a trade-off between the two, their development goes hand in hand. According to the ILO report, there will be a net increase of 18 million jobs across the globe as a result of environmentally sustainable measures taken in the production and use of energy. This net figure is based on the estimation that the resultant job losses of six million will eventually lead to an increase of 24 million jobs as greener practices are adopted. Of this, 14 million jobs created will be in Asia and the Pacific.
“The transition to a green economy will inevitably cause job losses in certain sectors as carbon and resource-intensive industries are scaled down, but they will be offset by new job opportunities,” the report said. However, the report emphasised that the net increase of 18 million jobs is dependent on a supportive policy framework to aid displaced workers and skill development programs to help ease them into jobs that require new skills. It mentioned that although India does have a specific body or council to address the skills development for green transition, it has no existing institutional mechanism to anticipate skills needs and adapt training provision. Of the 27 countries surveyed, India and seven others fall under this category. “Developing and emerging economies have relatively weaker institutional capacity for integrating skills and environmental sustainability,” the report said.
The report stressed on the urgency of economies adopting sustainable practices, adding, in 2013, humanity used 1.7 times the amount of resources and waste that the biosphere was able to regenerate and absorb. The report reads, “It is striking that in a context of scarce resources and limited ability to absorb waste, current patterns of economic growth rely largely on the extraction of resources, manufacturing, consumption and waste.” It explained this urgency from the perspective of the job market by connecting labour productivity to climate change.“Looking ahead, projected temperature increases will make heat stress more common, reducing the total number of working hours by 2% globally by 2030 and affecting workers in agriculture, and developing countries,” the report said.
Q. As per your understanding of the passage, which of the following can be said to be example/s of steps which contribute towards a green economy
I. The government announces tax incentives for those using public transport.
II. The government provides subsidy on diesel cars so that it becomes affordable
III. The government supports start-ups working on the development of electric cars.
Directions: Read the passage and answer the questions that follow:
More than three lakh workers will be employed in the solar and wind energy sectors to meet the country’s target of generating 175 gigawatts of electricity from renewable sources by 2022, an International Labour Organization (ILO) report said. The report titled, World Employment and Social Outlook (WESO) 2018: Greening with Jobs, quoted from a study conducted by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) and the Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC), on the changes in sectoral employment that will occur in order to meet India’s target. The study was based on surveys of solar and wind companies, developers and manufacturers.
“India is rapidly increasing its share of renewable energy sources, but still relies on coal, oil, natural gas, and the related carbon emissions for 80% of its electricity,” the report released on Tuesday said. This formed a small part of the report, which focused on the trajectory of the labour market in the backdrop of environmentally sustainable production practices. Tackling the misconception that green economies pave the way for economically undesirable outcomes, the report said rather than a trade-off between the two, their development goes hand in hand. According to the ILO report, there will be a net increase of 18 million jobs across the globe as a result of environmentally sustainable measures taken in the production and use of energy. This net figure is based on the estimation that the resultant job losses of six million will eventually lead to an increase of 24 million jobs as greener practices are adopted. Of this, 14 million jobs created will be in Asia and the Pacific.
“The transition to a green economy will inevitably cause job losses in certain sectors as carbon and resource-intensive industries are scaled down, but they will be offset by new job opportunities,” the report said. However, the report emphasised that the net increase of 18 million jobs is dependent on a supportive policy framework to aid displaced workers and skill development programs to help ease them into jobs that require new skills. It mentioned that although India does have a specific body or council to address the skills development for green transition, it has no existing institutional mechanism to anticipate skills needs and adapt training provision. Of the 27 countries surveyed, India and seven others fall under this category. “Developing and emerging economies have relatively weaker institutional capacity for integrating skills and environmental sustainability,” the report said.
The report stressed on the urgency of economies adopting sustainable practices, adding, in 2013, humanity used 1.7 times the amount of resources and waste that the biosphere was able to regenerate and absorb. The report reads, “It is striking that in a context of scarce resources and limited ability to absorb waste, current patterns of economic growth rely largely on the extraction of resources, manufacturing, consumption and waste.” It explained this urgency from the perspective of the job market by connecting labour productivity to climate change.“Looking ahead, projected temperature increases will make heat stress more common, reducing the total number of working hours by 2% globally by 2030 and affecting workers in agriculture, and developing countries,” the report said.
Q. Which of the following statements weakens the argument about the urgency of economies in adopting sustainable practices?
Directions : Read the passage carefully and answer the questions given below:
For generations, companies have been selling fair skin to young Indian women, promising better marriage and employment prospects. However, over the last few years, men have become a favoured target audience. This followed the realisation that the Indian alpha male, denied a choice in male-specific grooming products, had been using women’s fairness creams all along. Until the mid-2000s, deodorants and shaving creams were the only grooming products advertised for men. But India’s largest consumer goods companies sensed an opportunity, and launched a slew of fairness products for male consumers.
In India, as in other parts of the world, light skin is the culturally accepted and endorsed form of beauty, and children absorb this message at a young age. According to a 2015 research report by Nielsen, urban Indian men believe that fair skin can improve professional prospects. The cultural pressure to look fair, argues Kiran Khalap, branding expert and founder at communications consultancy Chlorophyll, is something inherent in our society, not manufactured by companies. “And it is certainly not restricted to India: China and Japan have had skin-whitening products for centuries, well before they met Western ‘white’ people,” he said. However, there is a growing awareness among consumers that companies are exploiting their insecurities, and critics have taken some of the biggest fairness brands, and the celebrities who endorse them, to task for their casual discrimination.
Earlier this month, Bollywood actor Abhay Deol took to Facebook to trounce his fellow actors who earn millions from endorsing fairness creams. This comes a few years after actress Nandita Das launched the “Dark is Beautiful” campaign to encourage Indians to embrace a wider definition of beauty. These efforts are slowly making a difference, increasing awareness and encouraging consumers to take pride in their natural skin tones. That means Indian companies will eventually have to change their approach. “My sense is that brands will wake up to the new reality, and you will see propositions reworked around clearer skin (and) glow, rather than pure fairness,” Leo Burnett’s Sinha said.
Rajesh Krishnamurthy, business head for the consumer product division at The Himalaya Drug Company, believes that over time the men’s grooming category will evolve to include a wider range of products, including those for normal skin, just like in the women’s skin care category. “Companies are increasingly realising that you cannot continue to bullshit consumers anymore; these are educated young men who will question what you sell to them,” said Shantanu Deshpande, co-founder and CEO of the male-grooming startup Bombay Shaving Company.
Q. With reference to the passage, why exactly was “Dark is beautiful” campaign initiated?
Directions: In this question, you need to replace the underline part of the sentence by the most suitable idiom/expression given as option.
You must be extra careful with even minor details with electrical work.
As part of the Financial Inclusion the following acts as an alternative to the Branch Banking.
______________ are financial instruments in which an investor lends money to a corporation or government for a specific length of time in exchange for regular interest payments.
Which among the following is used as an identifier of mobile money?
Which organization received the GeM award in the "Timely Payments (CPSEs)" category?
What is the aim of the NCC Integrated Software launched by Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh?
When will the United Nations Security Council hold its first-ever meeting on the threats of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Who has been named a minor planet by the International Astronomical Union (IAU)?
Which programming language is widely used for data analysis and scientific computing?
Speed of line printer is limited by the speed of