Sociology CUET PG Mock Test- 1 - CUET PG MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Sociology CUET PG Mock Test- 1
What is correct sequence of the research after the collection of data?
A. Screening of filled tool
B. Coding
C. Tabulation
D. Report writing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
According to 'Becker and Sarantakos', which one of the following is not the theoretical goal of Social Research ?
Which of the following is not true in the context of urbanisation?
Drug addiction is one of the most significant factors in-
Which among these are characteristics of ethnographic methods of data collection?
(A) Participant observation
(B) Adapted to meet the requirements of researchers with various view points on the nature of social reality
(C) Generates in-depth informations on the subjects under study
(D) Specific variables controlled by the researcher
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is an incorrect statement about the terms and classification used while conducting the process of research ?
Which of the following measures of central tendency is most affected by outliers?
According to ________ class distinctions exist because means of production are in the hands of only one class and that dominant class exploits the other classes
In which five year plan poverty alleviation has been included?
Tonnies's concept of Gemeinschaft is characterised by what kind of relationship?
Inequality of power and advantage is central for __________ because of the crucial place of stratification in the organisation of society.
Strong ideas of right and wrong which require certain actions and forbids others is:
Which of the following is an example of education as an agent of social change in India?
Integrating special students into overall educational program is called ________
Reasoning: Variances in wealth, education, ethnicity, and gender create unequal opportunities, solidifying societal hierarchies.
People under the class structure who are economically, politically and socially marginalised and excluded comprise the
Which of the following are true:
A. Max Weber is associated with Interpretive Sociology
B. Emile Durkheim is associated with Historical Materialism
C. Pierre Bourdieu is associated with Field Theory
D. Erving Goffman is associated with Symbolic Interactionism
Select the correct option from the given options:
Cultural pattern which is widespread among society's population is called:
Match List-I with List-II:
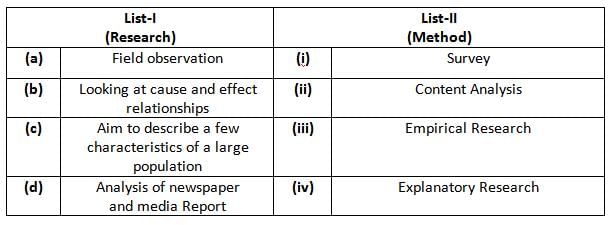
Select the correct codes from the options given below.
Which theory views that deviance and conformity result not so much from what people do as from how others respond to those actions?
Which among these is NOT a characteristic of secondary group?
Point out which one of the following is not a necessary quality of a 'good investigator' in a social problem?
Many of the social problems in modern India could be due to the neglect of:
Match List I with List II
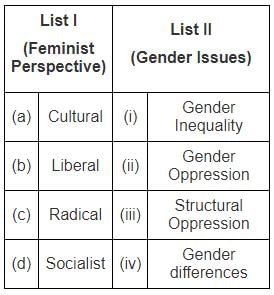
Choose the correct option:
Match List I with List II regarding forms of corruption and their descriptions:
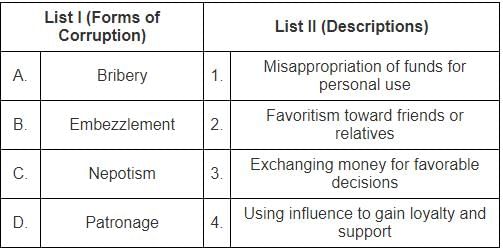
Choose the correct option from below:
Which of the following classes have been given reservation by the 73rd amendment of the Indian Constitution?
Which of the following denotes features of caste system?














