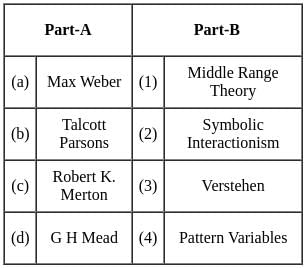
Answer: The correct answer is, (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
(a) Multiculturalism: This concept refers to the co-existence of diverse cultures within a single society. Multiculturalism recognizes and respects the presence of multiple cultural groups, their unique identities, traditions, and practices within a unified national or societal framework.
(b) Identity Politics: This term describes the advocacy for the interests of a particular group based on shared characteristics, such as race, ethnicity, gender, or sexuality. Identity politics involves the mobilization of group identities to assert rights, representation, and recognition in the political and social spheres.
(c) Cultural Relativism: This is the belief that cultures should be understood and evaluated on their own terms, without imposing external standards or judgments. Cultural relativism holds that cultural practices and beliefs are relative to the specific cultural context and should not be judged by universal or objective criteria.
(d) Assimilation: Assimilation refers to the process by which minority groups adopt the cultural norms, values, and practices of the dominant or majority group within a society. It involves the gradual absorption and integration of minority groups into the mainstream culture, often resulting in the loss of their distinct cultural identities.
Key PointsI. Multiculturalism:
- Recognition and acceptance of cultural diversity within a society
- Coexistence of multiple cultural groups with distinct identities, traditions, and practices
- Promotion of cultural pluralism and respect for cultural differences
- Policies and initiatives to support the preservation and expression of diverse cultures
- Challenges:
- Balancing unity and diversity
- Addressing potential conflicts and tensions between cultural groups
- Ensuring equal rights and opportunities for all cultural communities
- Integrating minority cultures into the mainstream society
II. Identity Politics:
- Advocacy for the rights and interests of specific social groups
- Based on shared characteristics such as race, ethnicity, gender, sexuality, or religion
- Mobilization of group identities for political representation and social recognition
- Challenging dominant narratives and power structures
- Key aspects:
- Collective identity formation
- Group solidarity and empowerment
- Demands for equal rights, resources, and opportunities
- Representation in decision-making processes
- Critiques of identity politics:
- Risk of essentialism and oversimplification of identities
- Potential for divisiveness and polarization
- Challenges in addressing intersectionality and multiple identities
III. Cultural Relativism:
- Belief that cultures should be understood and evaluated within their own cultural contexts
- Rejection of universal or objective standards for judging cultural practices
- Emphasis on respecting the diversity of cultural beliefs and norms
- Challenges:
- Reconciling cultural relativism with universal human rights and moral principles
- Addressing harmful or oppressive cultural practices
- Balancing respect for cultural differences with the need for social cohesion and integration
IV. Assimilation:
- Process of minority groups adopting the cultural norms, values, and practices of the dominant group
- Integration into the mainstream society through the adoption of dominant cultural elements
- Often involves the loss or dilution of minority cultural identities
- Critiques:
- Concerns about cultural erosion and loss of diversity
- Potential for marginalization and discrimination of non-assimilated groups
- Debates around the preservation of cultural heritage and traditions
Additional Information
- The concepts of multiculturalism, identity politics, cultural relativism, and assimilation are closely intertwined and have significant implications for contemporary societies. As globalization and migration patterns continue to reshape the demographic landscapes of nations, addressing issues of diversity, inclusion, and cultural coexistence has become paramount.
- Multiculturalism emerged as a response to the increasing diversity within societies, recognizing the need to accommodate and respect different cultural groups. However, the implementation of multicultural policies has faced challenges, such as ensuring equal opportunities, managing potential conflicts between cultural practices and societal norms, and fostering social cohesion amidst diversity.
- Identity politics has played a crucial role in amplifying the voices of marginalized groups and demanding recognition, representation, and equal rights. However, critics argue that identity politics can sometimes lead to the oversimplification of identities, neglecting intersectionality and the complex interplay of multiple identities within individuals and communities.
- Cultural relativism, while promoting respect for cultural differences, has been critiqued for its potential to condone harmful or oppressive cultural practices in the name of cultural preservation. Striking a balance between respecting cultural diversity and upholding universal human rights and moral principles remains an ongoing challenge.
- Assimilation, historically promoted as a means of integrating minority groups into the mainstream society, has faced criticism for its potential to erode cultural diversity and marginalize non-assimilated groups. Contemporary debates surrounding assimilation often center on finding a balance between respecting cultural heritage and promoting social cohesion.
- These concepts have significant implications for policymaking, education, and social discourse. Governments and institutions grapple with issues such as accommodating cultural practices in public spheres, promoting intercultural understanding and dialogue, and addressing discrimination and inequality based on cultural or identity markers.
- Moreover, the intersection of these concepts with broader societal dynamics, such as globalization, migration patterns, and power structures, further complexifies the discourse. As societies become increasingly diverse, the need for nuanced and inclusive approaches that balance the celebration of diversity with the promotion of shared values and social cohesion becomes ever more pressing.
- Ultimately, navigating the complexities of multiculturalism, identity politics, cultural relativism, and assimilation requires ongoing dialogue, critical reflection, and a willingness to address the challenges and opportunities that arise from the coexistence of diverse cultures within a shared societal framework.