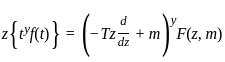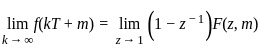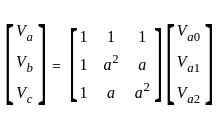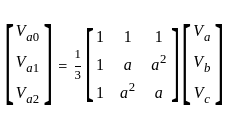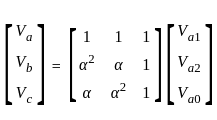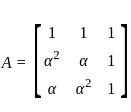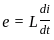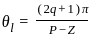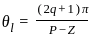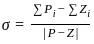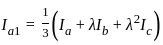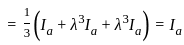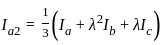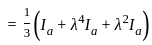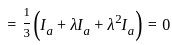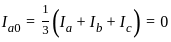TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 1
Let ?1(?) = ?2 and ?2(?) = z̅ be two complex variable functions. Here z̅ is the complex conjugate of z. Choose the correct answer.
If mean = 5. Variance = 10/3 of binomial distribution then number of trials is equal to.
If C is any simple closed curve enclosing the point z = z0, then the value of 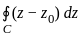
In the equivalent circuit of transformers the magnetizing circuit branch is drawn in parallel to supply voltage because
The ratio of hydraulic stress and volumetric strain is called _____.
A piece of ice is floating on water in a container. What will happen to the surface of water when whole ice piece melts:
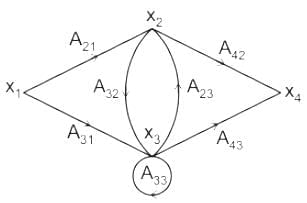
Which of the following equations holds true for the following signal flow graph?
The maximum number of input or output devices that can be connected to 8085 microprocessor are
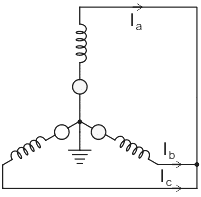
In the symmetrical component expression of voltages, we have
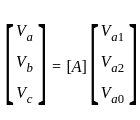
A coil of 0.5 H carries a current of 1 A. If the current is reversed in 1 millisecond, emf induced in the coil is
A unity feedback system has open-loop poles at s = -2 ± j 2, s = -1 and s = 0 and a zero at s = -3.
What are the angles made by the root-loci asymptotes with the real axis?
MOV A, C
RAR
RAR
RAR
RAR
MOV C, A
HLT
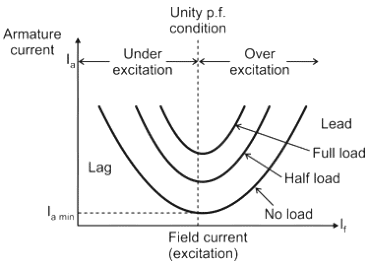
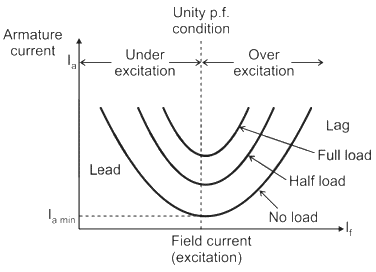
The program is for:A synchronous machine is connected to an infinite bus. The armature current change with field current for constant real power is
In which type of fault the negative and zero sequence currents are equal to zero
Let A and B be matrices of order 3. Which of the following is true?
void main ()
{
char far * farther, * farthest;
printf(“%d..%d”, sizeof(farther), sizeof(farthest));
}


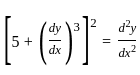 is
is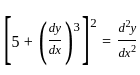
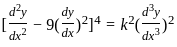
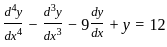
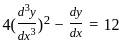
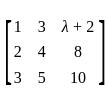 is singular, then λ equals
is singular, then λ equals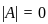 )
)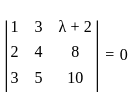

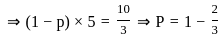
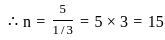
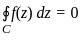
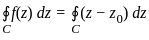
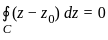
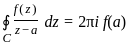
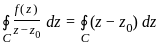
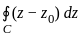 is
is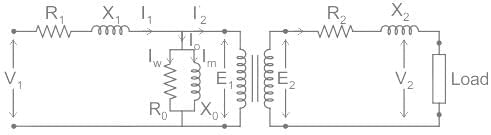
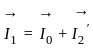
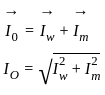
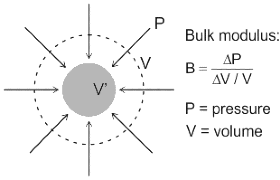
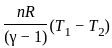
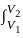
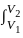
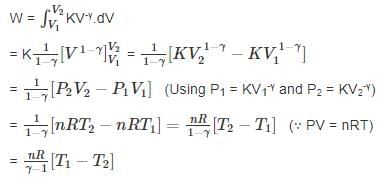
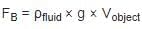
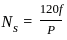
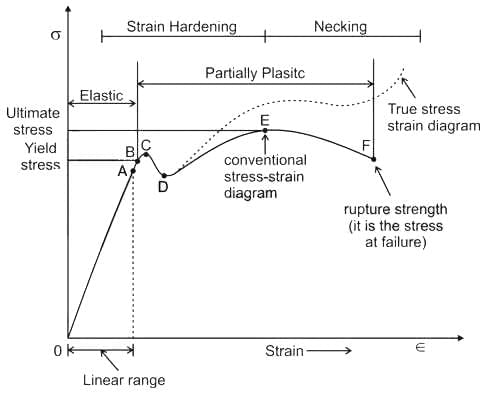
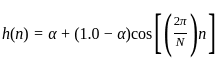
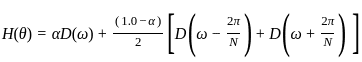
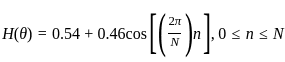
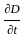 is based on
is based on