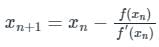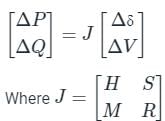Tes: Newton Raphson Method - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Tes: Newton Raphson Method
Which method is used as an advanced iterative method for generating appropriate solution steps to a real solution of a given nonlinear equation?
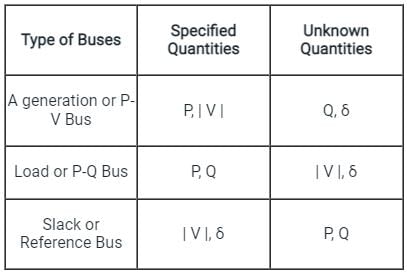
Consider a power system consisting of N number of buses. Buses in this power system are categorized into slack bus, PV buses and PQ buses for load flow study. The number of PQ buses is NL. The balanced Newton-Raphson method is used to carry out load flow study in polar form. H, S, M, and R are sub-matrices of the Jacobian matrix J as shown below:
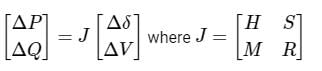
The dimension of the sub-matrix M is
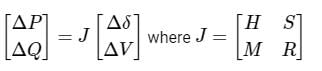
The dimension of the sub-matrix M is
In a 100 bus power system, there are 10 generators. In a particular iteration of Newton Raphson load flow technique (in polar coordinates), two of the PV buses are converted to PQ type. In this iteration,
A power system has 100 buses including 10 generator buses. For the load flow analysis using Newton-Raphson method in polar coordinates, the size of the Jacobian is
Determine the order of the Jacobian matrix (with one slack bus) for a 10 bus power system? (Assume 2 buses as voltage-controlled bus)
In a load flow problem solved by Newton-Raphson method with polar coordinates, the size of the Jacobian is 100 × 100. If there are 20 PV buses in addition to PQ Buses and a slack bus, the total number of buses in the system is _________.
A 183 – bus power system has 150 PQ buses and 32 PV buses. In the general case, to obtain the load flow solution using Newton – Raphson method in polar coordinates, the minimum number of simultaneous equations to be solved is_________.
A 10-bus power system consists of four generator buses indexed as G1, G2, G3, G4 and six load buses indexed as L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6. The generator-bus G1 is considered as slack bus, and the load buses L3 and L4 are voltage-controlled buses. The generator at bus G2 cannot supply the required reactive power demand, and hence it is operating at its maximum reactive power limit. The number of non-linear equations required for solving the load flow problem using Newton-Raphson method in polar form is ___________.