Test: Ascites, Hepatorenal Syndrome & Liver Cancer - NEET PG MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Ascites, Hepatorenal Syndrome & Liver Cancer
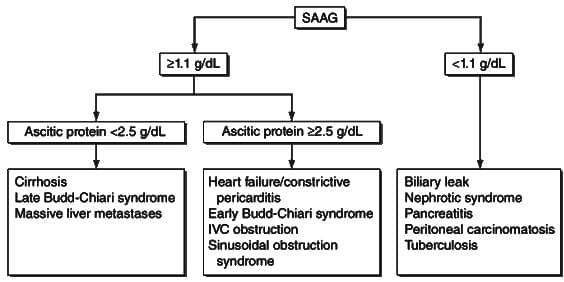
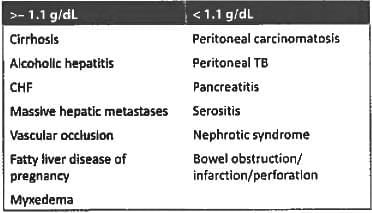
SAAG > 1.1% is seen in all cases of ascites except? (AIIMS Nov 2017)
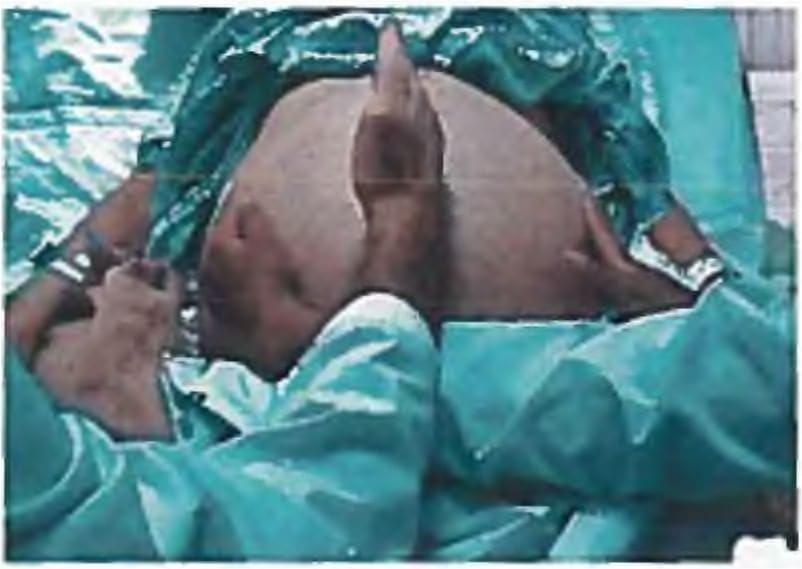
Which one of the following statements is TRUE regarding the clinical sign being elicited here? (AP PG 2016)

Maximum dose of spironolactone is: (APPG 2015)
A chronic liver disease patient with ascites and non bleeding varices presents with hematemesis and melena. What is the next step in management? (Jipmer Nov 2014)
Ascitic fluid with increased SAAG & ascitic protein > 2.5g/L is/are found in: (PGI May 2015)
Best Treatment of refractory ascites is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Child with S.A.A.G < 1.1 gm/dl: the probable diagnosis of the child is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Consider the following statements:
Ascites in cirrhosis of liver is due to (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
- Portal hypertension
- Hypoalbuminaemia
- Inappropriate ADH secretion
- Secondary hyper-aldosteronism
Which finding suggests a SVC obstruction? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which one of the following is NOT true about Ascites? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
First line of treatment in Ascites is: (PGI June 96)
Not a feature of hepatorenal syndrome: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Which of the following statement is incorrect with regard to Hepatorenal syndrome in a patient with cirrhosis (AI 2003)
Consider the following features Asian Male.
Alcoholic cirrhosis.
Hypervascular lesion during arterial phase of CT Portal vein thrombosis.
The above features are mostly suggestive of (AP PG 2016)
Which of the following is a vaccine preventable cancer? (JIPMER Nov 2014)
Best for management of 4 cm hepatocellular carcinoma in a cirrhotic patient with portal hypertension: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Most common liver tumour associated with OCP: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Best to diagnose a liver tumour? (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Most common benign tumor of the liver: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
All of the following are risk factors for Hepatocellular carcinoma except: (All India 2010)