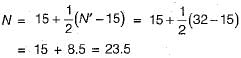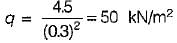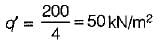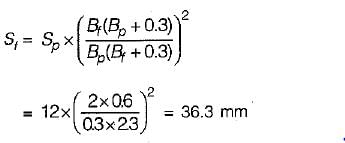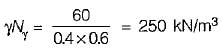Test: Bearing Capacity & Shallow Foundation - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Bearing Capacity & Shallow Foundation
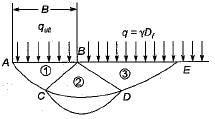
The net ultimate bearing capacity of a purely cohesive soil
Consider the following statements: increasing width of footing results in
1. Increase in settlement of a consolidating clay layer
2. Increase in bearing capacity of sandy soils
3. Decrease in bearing capacity of clays
Which of these statements is/are correct?
1. Increase in settlement of a consolidating clay layer
2. Increase in bearing capacity of sandy soils
3. Decrease in bearing capacity of clays
Which of these statements is/are correct?
If an SPT test gave the average blow count of 32 in fine sand below water table, then what is the corrected value of blow count?
Which factors influence the bearing capacity of a purely cohesionless soil?
1. Relative density of soil
2. Width and depth of footing
3. Unit weight of soil
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Match List-I (Types of foundation) with List-ll (Suitability) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Spread footings
B. Under reamed piles
C. Raft foundation
D. Deep foundation
List-ll
1. Soft clay for 20 m followed by hard rock stratum
2. Up to 3 m black cotton soil followed by medium dense sand
3. Compact sand deposit extending to great depth
4. Loose sand extending to great depth
A test plate 30 cm square, settles by 12 mm under a load of 4.5 kN in a sandy soil. By how much will a footing 2 m x 2 m subjected to a load of 200 kN settle?
In which one of the following zones is a logarithmic spiral shape of failure surface assumed in the case of bearing capacity analysis of c-ϕ soils?
The bearing capacity factors Nc, Nq and Ny are functions of
When a load test was conducted by putting a 60 cm square plate on top of a sandy deposit, the ultimate bearing capacity was observed as 60 kN/m2. What is the ultimate bearing capacity for a strip footing of 1.2 m width to be placed on the surface of the same soil?
The ultimate bearing capacity of a square footing on surface of a saturated clay having unconfined compression strength of 50 kN/m2 (using Skempton’s equation) is