Test: Biology - 2 - MCAT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test MCAT Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Biology - 2
If both parents have one recessive allele for blue eyes and one dominant allele for brown eyes, what is the percentage chance of an offspring having blue eyes?
Which option is something that could be detected by a proprioceptive sensor?
According to the attached passage, what event would need to occur to slow the signal to the respiratory centers?
Hypoxia is a term used to describe a set of symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and confusion, that arise due to oxygen deprivation. When visiting the Rocky Mountains in the US, where the partial pressure of oxygen is approximately 15% lower than what one is accustomed to on the coast, these symptoms can be induced. The body has a limited tolerance for variations in environmental oxygen levels as it lacks a significant capacity to store oxygen, which is continuously consumed to maintain energy homeostasis.
In response to oxygen deprivation, the body increases the rate of breathing and the volume of each breath. This adjustment is part of a negative feedback loop that helps maintain homeostasis. The carotid body, located inside the carotid artery, serves as the sensor for detecting oxygen concentrations. The information gathered by the carotid body is then processed in the respiratory centers (RCs) of the brainstem's medulla. Ultimately, the output of this feedback loop is directed to the diaphragm, which plays a key role in respiration.
Q. An increase in the concentration of ‘__’ slows down or stops a chemical reaction in a negative feedback loop in a biological system. (You may consult the attached passage.)
Hypoxia is a term used to describe a set of symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and confusion, that arise due to oxygen deprivation. When visiting the Rocky Mountains in the US, where the partial pressure of oxygen is approximately 15% lower than what one is accustomed to on the coast, these symptoms can be induced. The body has a limited tolerance for variations in environmental oxygen levels as it lacks a significant capacity to store oxygen, which is continuously consumed to maintain energy homeostasis.
In response to oxygen deprivation, the body increases the rate of breathing and the volume of each breath. This adjustment is part of a negative feedback loop that helps maintain homeostasis. The carotid body, located inside the carotid artery, serves as the sensor for detecting oxygen concentrations. The information gathered by the carotid body is then processed in the respiratory centers (RCs) of the brainstem's medulla. Ultimately, the output of this feedback loop is directed to the diaphragm, which plays a key role in respiration.
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be slowed down or shut down by the addition of an inhibitor. The reversible inhibition action of enzymes is considered competitive when the enzyme binds ____.
Q. When human cells cannot keep up with oxygen demand and need to create ATP anaerobically, which process is used? (You may consult the attached passage and graphics.)
Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of both plant and animal cells because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell. Cellular respiration is the process of making ATP using the chemical energy found in glucose and other nutrients. In mitochondria, this process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, the carbon dioxide that you exhale with every breath comes from the cellular reactions that produce carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Mitochondria are oval-shaped, double membrane organelles that have their own ribosomes and DNA. Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The inner layer has folds called cristae. The area surrounded by the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. The cristae and the matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
Dinitrophenol (DNP) was used in the manufacture of munitions in World War I. In the 1930s, it was used as a weight loss drug. Use in the U.S. cannot be regulated by the FDA because DNP is considered a dietary supplement. Attempts to ban the drug in the U.K. following the death of four users in 2015 failed in Parliament. DNP is a small molecule that is soluble in the mitochondrial inner membrane. The hydroxyl group reversibly dissociates a proton.
Q. It is believed that Dinitrophenol (DNP) can only impact oxidative phosphorylation. Considering this fact, why would it not impact glycolysis? (You may consult the attached passage and graphics.)
Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of both plant and animal cells because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell. Cellular respiration is the process of making ATP using the chemical energy found in glucose and other nutrients. In mitochondria, this process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, the carbon dioxide that you exhale with every breath comes from the cellular reactions that produce carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Mitochondria are oval-shaped, double membrane organelles that have their own ribosomes and DNA. Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The inner layer has folds called cristae. The area surrounded by the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. The cristae and the matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
Dinitrophenol (DNP) was used in the manufacture of munitions in World War I. In the 1930s, it was used as a weight loss drug. Use in the U.S. cannot be regulated by the FDA because DNP is considered a dietary supplement. Attempts to ban the drug in the U.K. following the death of four users in 2015 failed in Parliament. DNP is a small molecule that is soluble in the mitochondrial inner membrane. The hydroxyl group reversibly dissociates a proton.
Q. Considering the action of cyanide, what would be the most likely cause of death in a cyanide poisoning? (You may consult the attached passage and graphics.)
Mitochondria (singular = mitochondrion) are often called the “powerhouses” or “energy factories” of both plant and animal cells because they are responsible for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the cell’s main energy-carrying molecule. ATP represents the short-term stored energy of the cell. Cellular respiration is the process of making ATP using the chemical energy found in glucose and other nutrients. In mitochondria, this process uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. In fact, the carbon dioxide that you exhale with every breath comes from the cellular reactions that produce carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Mitochondria are oval-shaped, double membrane organelles that have their own ribosomes and DNA. Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins. The inner layer has folds called cristae. The area surrounded by the folds is called the mitochondrial matrix. The cristae and the matrix have different roles in cellular respiration.
Dinitrophenol (DNP) was used in the manufacture of munitions in World War I. In the 1930s, it was used as a weight loss drug. Use in the U.S. cannot be regulated by the FDA because DNP is considered a dietary supplement. Attempts to ban the drug in the U.K. following the death of four users in 2015 failed in Parliament. DNP is a small molecule that is soluble in the mitochondrial inner membrane. The hydroxyl group reversibly dissociates a proton.
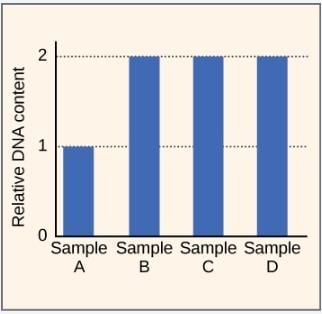
Q. Based on the attached passage and graphic, which of the following cycles is Sample A currently in, based on the relative DNA content of the sample?
The Cell Cycle:
The cell cycle is a carefully regulated sequence of events that involves cell growth and division, resulting in the production of two daughter cells. Cells progress through distinct stages of growth, DNA replication, and division to generate two identical cells. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase involves cell growth and DNA replication, while the mitotic phase encompasses the separation of replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents, leading to cell division.
In a research study focusing on cell division, scientists cultivate human cells undergoing synchronous division using thymidine. This causes the cells to pause at the G1G1 boundary. Subsequently, the cells are transferred to a thymidine-free medium, which releases the block and allows the cells to resume dividing. Four different samples (A-D) are taken at various time points after thymidine removal to measure the DNA content of the cells. The results for these samples are presented in the graph.
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome:
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS1) is a rare inherited condition associated with an increased susceptibility to cancer. This syndrome is linked to mutations in the tumor suppressor gene that encodes the transcription factor p53, which plays a crucial role at the G1 checkpoint of the cell cycle. When damaged DNA is detected, p53 halts the progression of the cell cycle. As p53 levels rise, it triggers the production of p21, a protein that enforces the cell cycle arrest. Another form of Li-Fraumeni syndrome, known as LFS2, is believed to be caused by a mutation in the CHK2 gene, which also functions as a tumor suppressor. CHK2 regulates the activity of p53 in the cell cycle
Q. Which of the following represents the correct sequence of phases in mitosis? (You may consult the attached passage and graphic.)
The Cell Cycle:
The cell cycle is a carefully regulated sequence of events that involves cell growth and division, resulting in the production of two daughter cells. Cells progress through distinct stages of growth, DNA replication, and division to generate two identical cells. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase involves cell growth and DNA replication, while the mitotic phase encompasses the separation of replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents, leading to cell division.
In a research study focusing on cell division, scientists cultivate human cells undergoing synchronous division using thymidine. This causes the cells to pause at the G1G1 boundary. Subsequently, the cells are transferred to a thymidine-free medium, which releases the block and allows the cells to resume dividing. Four different samples (A-D) are taken at various time points after thymidine removal to measure the DNA content of the cells. The results for these samples are presented in the graph.
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome:
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS1) is a rare inherited condition associated with an increased susceptibility to cancer. This syndrome is linked to mutations in the tumor suppressor gene that encodes the transcription factor p53, which plays a crucial role at the G1 checkpoint of the cell cycle. When damaged DNA is detected, p53 halts the progression of the cell cycle. As p53 levels rise, it triggers the production of p21, a protein that enforces the cell cycle arrest. Another form of Li-Fraumeni syndrome, known as LFS2, is believed to be caused by a mutation in the CHK2 gene, which also functions as a tumor suppressor. CHK2 regulates the activity of p53 in the cell cycle

Q. p53 acts at the G1 checkpoint. If genetic mutations are found, p53 will not allow the cell to proceed to the next step of the cell cycle, which would be ____. (You may consult the attached passage and graphic.)
The Cell Cycle:
The cell cycle is a carefully regulated sequence of events that involves cell growth and division, resulting in the production of two daughter cells. Cells progress through distinct stages of growth, DNA replication, and division to generate two identical cells. The cell cycle consists of two main phases: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase involves cell growth and DNA replication, while the mitotic phase encompasses the separation of replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents, leading to cell division.
In a research study focusing on cell division, scientists cultivate human cells undergoing synchronous division using thymidine. This causes the cells to pause at the G1G1 boundary. Subsequently, the cells are transferred to a thymidine-free medium, which releases the block and allows the cells to resume dividing. Four different samples (A-D) are taken at various time points after thymidine removal to measure the DNA content of the cells. The results for these samples are presented in the graph.
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome:
Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS1) is a rare inherited condition associated with an increased susceptibility to cancer. This syndrome is linked to mutations in the tumor suppressor gene that encodes the transcription factor p53, which plays a crucial role at the G1 checkpoint of the cell cycle. When damaged DNA is detected, p53 halts the progression of the cell cycle. As p53 levels rise, it triggers the production of p21, a protein that enforces the cell cycle arrest. Another form of Li-Fraumeni syndrome, known as LFS2, is believed to be caused by a mutation in the CHK2 gene, which also functions as a tumor suppressor. CHK2 regulates the activity of p53 in the cell cycle

Respiratory patients are sometimes placed in the ____ position to help with breathing, which means the patient would be placed lying face down on the bed.
|
45 tests
|














