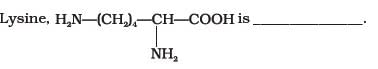Test: Biomolecules - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Biomolecules
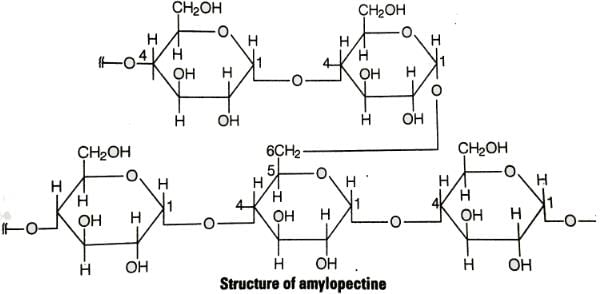
Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1-C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.
Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals?
Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives _________.
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of protein is stabilised by :
Which of the following is NOT a culinary use of oil in the food industry?
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ____________.
DNA and RNA contain four bases each. Which of the following bases is not present in RNA?
Which of the following B group vitamins can be stored in our body?
Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
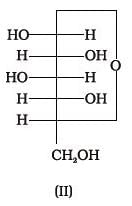
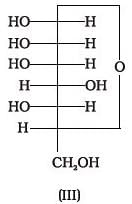
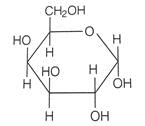
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
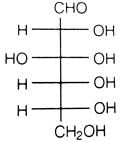
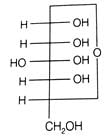
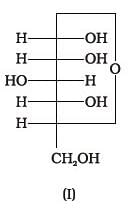
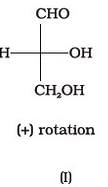
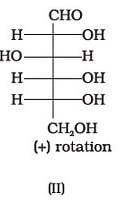
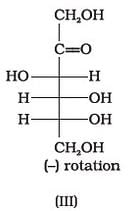
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
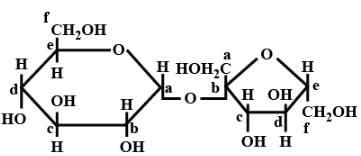
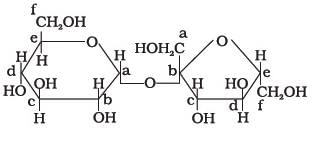
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.
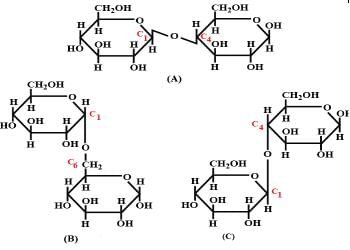
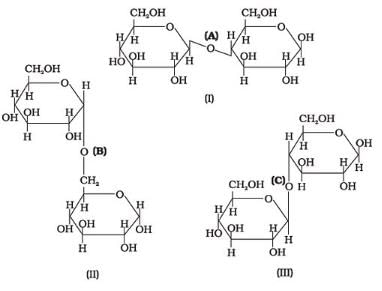
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is a __________.
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are :
(Multiple Answer Correct)
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymer of glucose?
Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)?
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by ___________.