Test: C.O.P.D & Bronchiectasis and Suppurative Lung Diseases- 1 - NEET PG MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: C.O.P.D & Bronchiectasis and Suppurative Lung Diseases- 1
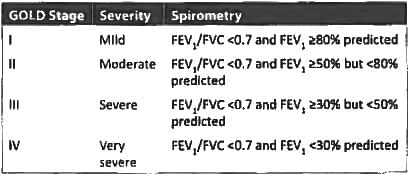
Gold Criteria for very severe COPD is defined as? (Recent Pattern 2018)
Which is correct about ILD? (Recent Pattern Questions)
Increased Reid index is classically associated with? (APPG 2016)
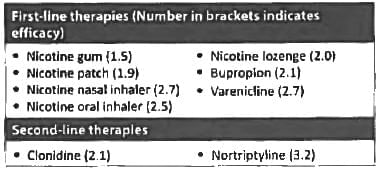
Which are the drugs used for smoking cessation? (Bihar PG 2015)
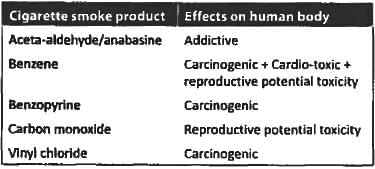
Which component of cigarette smoke is responsible for CAD? (Recent Question 2015-16)
Smoking causes all cancers EXCEPT? (Recent Question 2015-16)
Central bronchiectasis is seen with? (Recent Pattern 2015-16)
Bronchiectasis sicca is seen with: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
All are complications of bronchiectasis except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
All are seen in emphysema except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Emphysema presents with all except: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
The drug varenicline is used in: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
False about emphysema is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Chronic Cor pulmonale is seen in all except: (PGI-Dec-04)
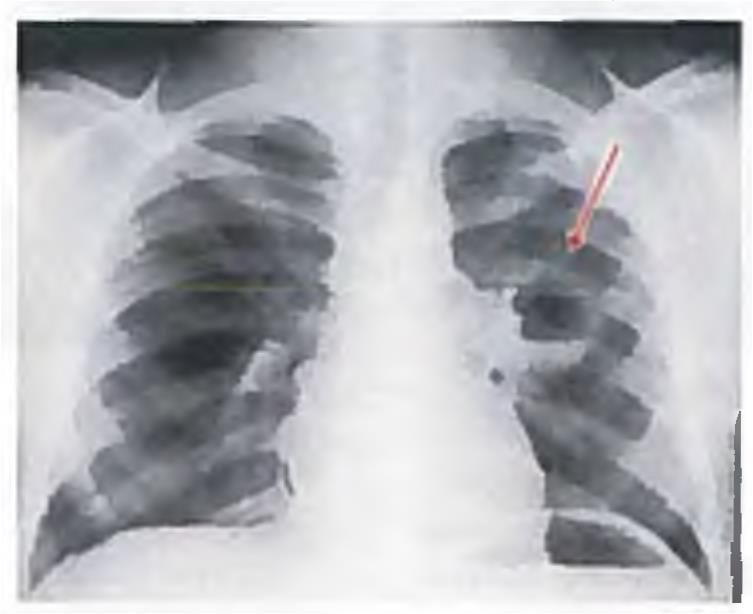
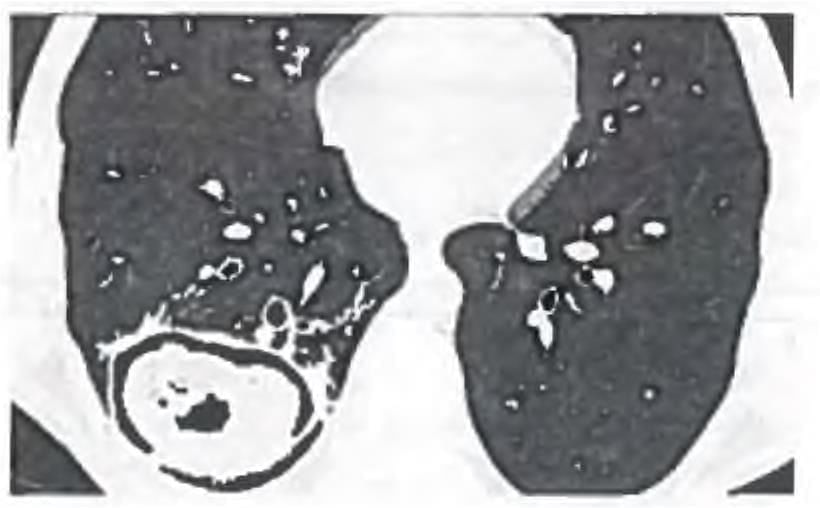
A 40-year-old male alcoholic presents with features of fever and productive cough that increases with posture change. CXR of the patient is given below. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient? (AIIMS Nov 2016)