Test: C.O.P.D & Bronchiectasis and Suppurative Lung Diseases- 2 - NEET PG MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: C.O.P.D & Bronchiectasis and Suppurative Lung Diseases- 2
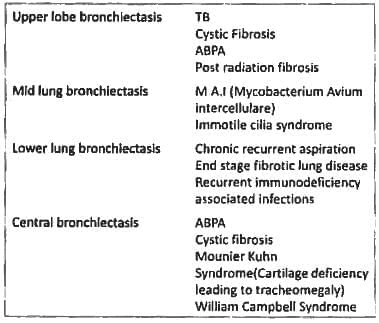
Most common type of bronchiectasis? (Recent Question 2016-17)
Mid lung field bronchiectasis is seen with? (Recent Question 2016-17)
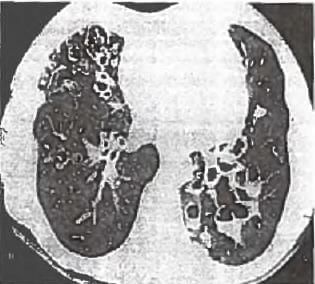
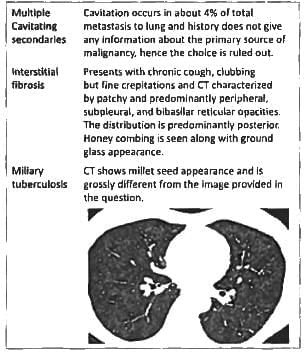
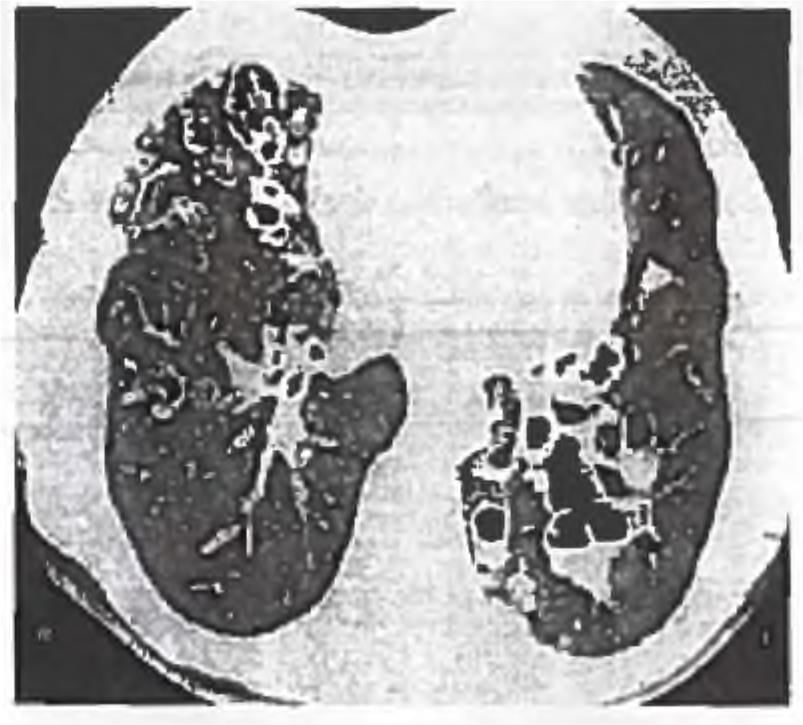
This patient came with chronic productive cough and clubbing and coarse rales. What is the diagnosis of the CT scan above? (APPG 2015)


IOC for Bronchiectasis: (Recent Question 2015-16)
Chest X-ray in a 45 yr old patient shows cavity in upper lobe of lung. Next investigation for diagnosis is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Most likely precursor to bronchiectasis is: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Best method for detecting minimal bronchiectasis is:
In a patient with COPD, with low spo2 at rest best management option is? (Recent Question 2015-16)
Most common cause of lung abscess in comatose patient? (Recent Pattern 2015-16)
Ultrastructural abnormalities reported in immotile cilia syndrome are: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
In a patient with smoking history, which is important? (Recent Question 2015-16)
Parents of a child with bronchiectasis may give a past history of: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Not a CT finding in bronchiectasis: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)
Bronchiectasis is most common in: (Recent Pattern 2014-15)