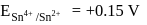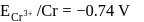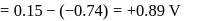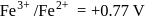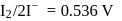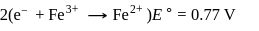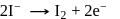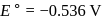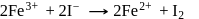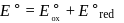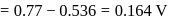Test: Cells and Electrode Potential - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Cells and Electrode Potential
An electrolytic cell contains a solution of 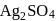 and has platinum electrodes. A current is passed until
and has platinum electrodes. A current is passed until 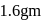 of
of 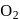 has been liberated at anode. The amount of silver deposited at cathode would be
has been liberated at anode. The amount of silver deposited at cathode would be
Which statement best defines an oxidising agent?
A standard hydrogen electrode has zero electrode potential because
A cell is prepared by dipping a chromium rod in 1M Cr2(SO4)3 solution and an iron rod in 1M FeSO4 solution. The standard reduction potentials of Chromium and Iron electrodes are -0.75 V and -0.45 V respectively. What will be the standard EMF of the cell?
A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1MY− and MZ− at 25∘C. If the reduction potential of Z > Y > X, then,
On the basis of the following 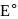 values, the strongest oxidizing agent is:
values, the strongest oxidizing agent is:
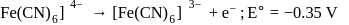
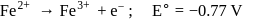
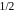 is represented by
is represented by
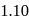 volt. The maximum electrical work (in
volt. The maximum electrical work (in 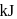 ) obtained from the Daniell cell is
) obtained from the Daniell cell is
The standard 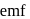 for the given cell reaction,
for the given cell reaction, 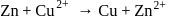 is
is 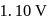 at
at 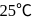 . The
. The 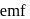 for the cell reaction, when
for the cell reaction, when 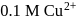 and
and 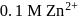 solutions are used, at
solutions are used, at 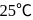 , is
, is
(Use 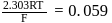 )
)
The standard reduction potentials at 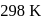 for the following half reactions are given against each
for the following half reactions are given against each 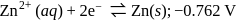
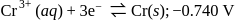
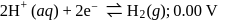
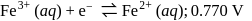
Which is the strongest reducing agent?
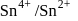 couple is
couple is 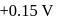 and that for the
and that for the 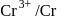 couple is
couple is 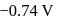 . These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be:
. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be:
A solution contains Fe2+, Fe3+ and I− ions. This solution was treated with iodine at 35∘C.E∘ for Fe3+/Fe2+ is +0.77 V and E∘ for I2/2I− = 0.536 V
The favourable redox reaction is :


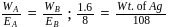
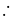 Wt. of
Wt. of 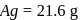

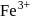 is strongest oxidising agent. More the positive value of
is strongest oxidising agent. More the positive value of 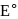 , more is the tendency to get oxidized. Thus correct option is (c).
, more is the tendency to get oxidized. Thus correct option is (c).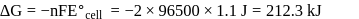 .
.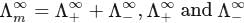
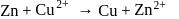
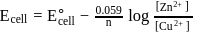
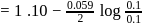
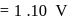
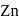 is highest hence strongest reducing agent.
is highest hence strongest reducing agent.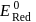 and oxidises
and oxidises 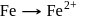
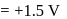 .
.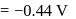 .
.