Test: Cement, Mortar & Lime - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Civil Engineering - Test: Cement, Mortar & Lime - 3
Consider the following statements:
The effect of air entrainment in concrete is to
1. increase resistance to freezing and thawing
2. improve workability
3. decrease strength
Which of these statements are correct?
The effect of air entrainment in concrete is to
1. increase resistance to freezing and thawing
2. improve workability
3. decrease strength
Which of these statements are correct?
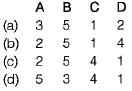
Match List-I (Property of cement) with List-ll (Testing apparatus) and select the correct answer using the codes give below the lists:
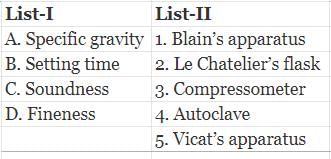
Codes:
Consider the following statements: High early strength of cement is obtained as a result of
1. fine grinding
2. decreasing the lime content
3. burning at higher temperatures
4. increasing the quantity of gypsum
Which of these statements are correct
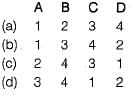
Match List-I with List-ll and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
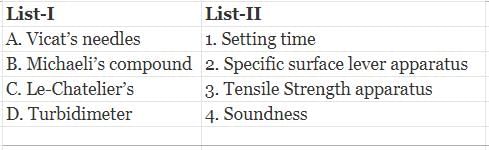
Codes:
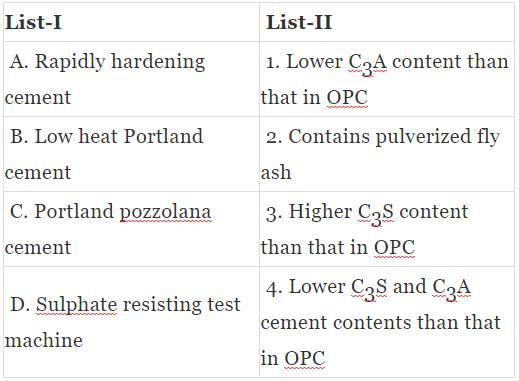
Match List-I (Type of cement) with List-II (Property/characteristics) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Match List-I (Apparatus) with List-ll (Purpose) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:

Codes:

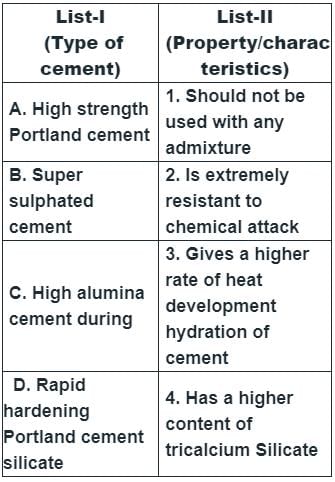
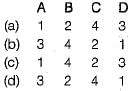
Match List-I (Type of Cement) with List-ll (Characteristics) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
Codes:
Consider the following statements: Low percentage of C3S and high percentage of C2S in cement will result in
1. higher ultimate strength with less heat generation
2. rapid-hardening
3. better resistance to chemical attack
Which of these statements are correct?
Consider the following statements:
"When cement is tested /for setting time; on gauging it shows quick setting. This phenomenon known as "Flash set" of cement is due to the presence of high
1. Tricalcium Aluminate (C3A) in cement
2. Alkalies in cement .
3. Tricalcium Silicate (C3S) in cement.
Which of these statements are correct?
Match List-I (Cement) with List-lI (Characteristic) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

Codes:

Consider the following statements:
1. Addition of a small quantity of slaked lime to Portland cement in cement mortar increases the plasticity of the mortar.
2. Light weight mortar is prepared by mixing cement and finely crushed fire bricks with water,
3. Fire resistant mortar is prepared by mixing aluminous cement and finely ground china clay wares with water.
Which of these statements are correct?
Which type of following cement is used for mass concrete work
Low heat cement contains lower percentage of which of the following
Specific surface of portland cement should not be less than
Loss on ignition in portland cement shall not be more than
Which of the following is correct if they are arranged in decreasing order of heat of hydration



















