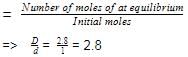Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Degree of Dissociation & Vapour Density - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Degree of Dissociation & Vapour Density
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the following equilibrium,
PCl5(g)  PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g)
Vapour density is found to be 100 when 1 mole of PCI5 is taken in 10 dm3 flask at 300 K. Thus, equilibrium pressure is
choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
 PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g)Vapour density is found to be 100 when 1 mole of PCI5 is taken in 10 dm3 flask at 300 K. Thus, equilibrium pressure is
For the equilibrium, N2O4(g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
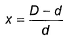 here, d is experimental vapour density and D is theoretical vapour density. Thus, for the equilibrium
here, d is experimental vapour density and D is theoretical vapour density. Thus, for the equilibrium
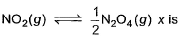
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)In the following equilibrium at 400 K in 1 dm3 flask,
COCl2 (g) CO(g) + Cl2 (g),
CO(g) + Cl2 (g),
ratio of theoretical and experimental vapour density is 1.4. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is
 CO(g) + Cl2 (g),
CO(g) + Cl2 (g),ratio of theoretical and experimental vapour density is 1.4. Thus, equilibrium constant Kc is
A(g) is 100% converted into B according to the reaction,
A(g)  3b(g)
3b(g)
Value of at this point is
In the dissociation of PCI5(g)into PCI3(g)and Cl2(g), values of(1 + x)have been plotted versus D/d. Thus, correct graph is
CCI4(g) dissociates 50% into gaseous free radicals at 1000 K and at equilibrium experimental vapour density is found to be 38.5. Thus, CCI4(g) dissociates under the given conditions to
0.578 g N2O4(g) dissociates into 1dm3 flask at 308 K to give a pressure of 24.12 kPa.
N2O4 (g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Thus, degree of dissociation of N2O4 is
SO3(g)is partially dissociated into SO2(g)and O2(g) at 900K and 1 atm as:
The density of the equilibrium mixture was found to be 0.866 gdm-3. Thus, degree of dissociation of SO3 (g) is
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-12) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Vapour density of the equilibrium mixture of NO2 and N2O4 is found to be 40 for the gaseous phase equilibrium at 400 K in 1 dm3 flask.
N2O4 (g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Q. Equilibrium Constant Kc is
Passage I
Vapour density of the equilibrium mixture of NO2 and N2O4 is found to be 40 for the gaseous phase equilibrium at 400 K in 1 dm3 flask.
N2O4 (g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Q. Percentage of N02 in the mixture by volume is
Passage II
COCI2 (phosgene) gas dissociates according to
COCl2 (g)  CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
At 101.325 kPa and at 724 K density of the gas mixture is 1.162 g dm-3.
Q. Observed molar mass of the gaseous mixture is
Passage II
COCI2 (phosgene) gas dissociates according to
COCl2 (g)  CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
CO(g) + Cl2 (g)
At 101.325 kPa and at 724 K density of the gas mixture is 1.162 g dm-3.
Q. Equilibrium constant Kp is
Direction (Q. Nos. 21 and 22) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. In the following hypothetical equilibrium,
Values of D/d (along y-axis) have been plotted
versus a (along x-axis.)
α = degree of dissociation
d = experimental vapour density
D = theoretical vapour density
Q. What is the value of D/d at the point A corresponding to α = 1 ?
Direction (Q, Nos. 14 - 15) These questions are subjective in nature, need to be solved completely on notebook.
NO2 is 40.0% of the total volume at 300 K in the following equilibrium,
N2O4 (g)  2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
Calculate the ratio of vapour density in the absence and presence of dissociation.
PCI5(g) dissociates according to the reaction at 523 K.
PCl5(g)  PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g) KP = 1.78 atm
PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g) KP = 1.78 atm
Compute the density of the equilibrium mixture in g dm-3 at 1 atm pressure.