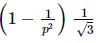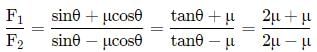Test: Common forces in mechanics (June 6) - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Common forces in mechanics (June 6)
Which of the following statements is correct about friction?
Which of the following is a self adjusting force?
Which one of the following can also act as a lubricant in machines?
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 30∘ with the horizontal, it takes time 20s. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it takes time 20p s, where p is some number greater than 1. The coefficient of friction between the body and the rough plane is
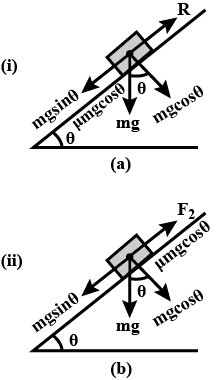
The minimum force required to start pushing a body up a rough (frictional coefficient μ) inclined plane is F1 while the minimum force needed to prevent it from sliding down is F2. If the inclined plane makes an angle θ from the horizontal such that tan θ = 2μ then the ratio F1/F2 is :
The coefficient of static friction between the box and the train's floor is 0.2. The maximum acceleration of the train in which a box lying on its floor will remain stationary is (Take g = 10 ms−2)
A block of mass 1 kg lies on a horizontal surface in a truck. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.6. If the acceleration of the truck is 5ms−2. The frictional force acting on the block is then
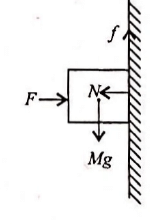
A block of mass M is held against a rough vertical wall by pressing it with a finger. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is μ and the acceleration due to gravity is g, what is the minimum force required to be applied by the finger to hold the block against the wall?
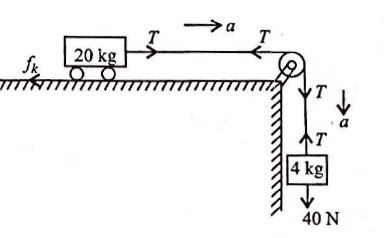
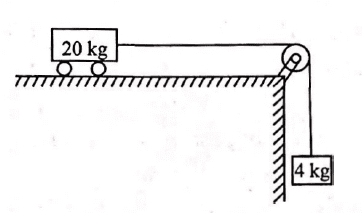
A trolley of mass 20kg is attached to a block of mass 4kg by a massless string passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between trolley and the surface is 0.02, then the acceleration of the trolley and block system is(Take g = 10ms−2)



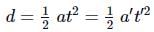 (∵ u = 0)
(∵ u = 0)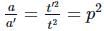 (∵ t′ = 20ps,t=20s)
(∵ t′ = 20ps,t=20s) 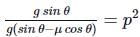 (Using (i) and (ii))
(Using (i) and (ii))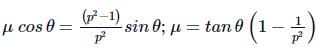 Here, θ=30∘ ∴ μ =
Here, θ=30∘ ∴ μ =