Test: Current & Voltage in an Inductive Circuit, Capacitive Circuit - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Current & Voltage in an Inductive Circuit, Capacitive Circuit
Inductor does not allow sudden changes in?
In case of Inductive circuit, Frequency is ______________ to the current.
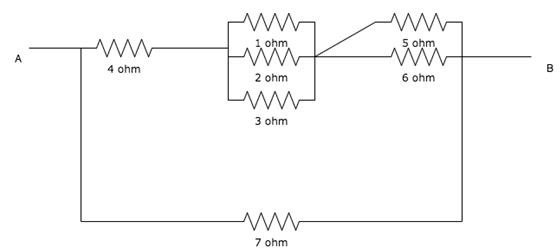
Calculate the resistance between A and B.
Pure inductive circuit
An induced emf is said to be ___________
In a pure inductive circuit, the power factor is?
Among the following, which is the right formula for inductance?
Among the following, which is the right formula for inductance?
If the current in a coil having a constant inductance of L henrys grows at a uniform rate, what is the value of the average current?
Find the average current in an inductor if the total current in the inductor is 30A.
What happens to the voltage in a capacitive circuit when the frequency increases?
When voltage across a capacitor increases, what happens to the charge stored in it?
What happens to the current flow in a fully charged capacitor?
What is the correct formula for capacitive reactance?
Calculate the capacitance of a capacitor that stores 80microC of charge and has a voltage of 4V.
What happens to the current in a capacitive circuit when the frequency increases?
Calculate the current in the capacitor having 2V supply voltage and 3F capacitance in 2seconds.
If 2V is supplied to a 3F capacitor, calculate the charge stored in the capacitor.
A 30 microF capacitor is connected across a 400V, 50Hz supply. Calculate the capacitive reac-tance.
A 30 microF capacitor is connected across a 400V, 50Hz supply. Calculate the current.














