Test: Design of Traffic Intersections - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Design of Traffic Intersections
Which of the following is not an intersection at grade?
A well-designated signalized intersection is one in which the
An intersection that is provided for different levels of road is called __________
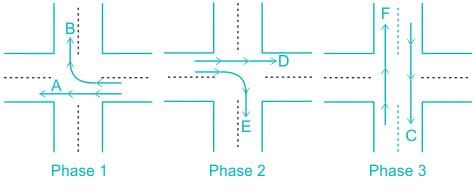
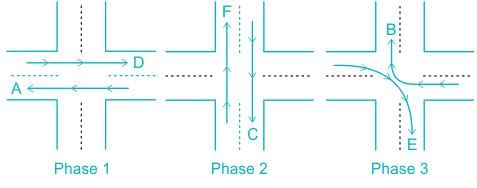
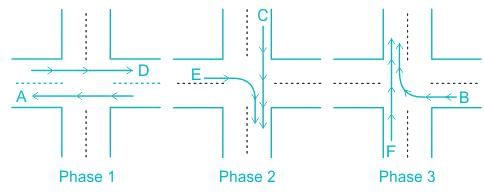
A 3 phase traffic signal at a 4-legged intersection is designed for flow as show below
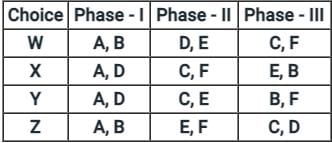
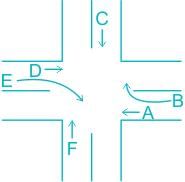
There are 6 groups of flows identified by the alphabets, A through F. among these A,C,D and F are through flows, and B and E are right turnings. Identify which phasing scheme is not recommended
If the velocity of a vehicle is 60kmph and the other vehicle velocity is 20kmph, then the relative velocity is?
Which of the following is not a correct statement with respect to basic requirements of intersection at grade?
If the angle of merging is low, then the relative speed will be __________
The basic traffic manoeuvres in a traffic stream may be represented by ______.
If an additional pavement is provided for lane change, then that intersection is called __________
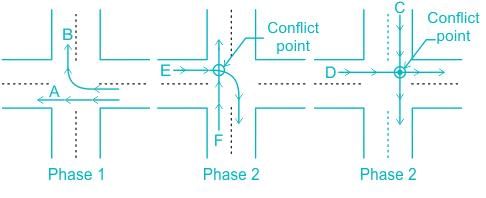
The number of "right turn-through" traffic conflict points in a 2-lane-2-way uncontrolled intersection are ____.