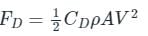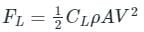Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Tests > Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering > Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering - Test: Drag Force & Lift Force
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering preparation. The Test: Drag Force & Lift Force questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus.The Test: Drag Force & Lift Force MCQs are made for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force below.
Solutions of Test: Drag Force & Lift Force questions in English are available as part of our Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering for Civil Engineering (CE) & Test: Drag Force & Lift Force solutions in
Hindi for Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Drag Force & Lift Force | 10 questions in 30 minutes | Mock test for Civil Engineering (CE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study Fluid Mechanics for Civil Engineering for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 2
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 3
ln which of the following the friction drag is generally larger than pressure drag?
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 3
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 4
Friction drag is generally larger than the pressure drag in _______.
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 4
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 5
What are the effects on the body with mass immersed in a fluid which is under motion?
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 5
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 6
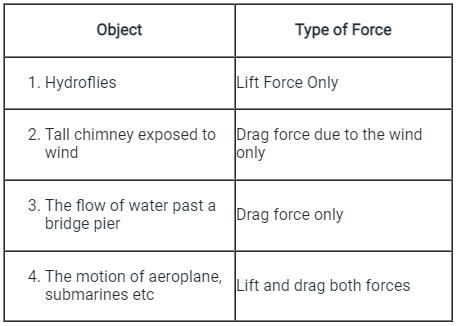
Which one of the following is an example of bodies where both drag and lift forces are produced?
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 6
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 7
The component of the total force in the direction of motion is called ________.
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 7
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 8
A plate of negligible thickness is held perpendicular to the flow direction. The drag force experienced on the plate is mainly due to:
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 8
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 9
A forceful pull experienced by the flat plate when fluid flows on it is called _______.
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 9
Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 10
The drag and lift forces experienced by an object placed in a fluid stream are due to
Detailed Solution for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force - Question 10
|
54 videos|97 docs|110 tests
|
Information about Test: Drag Force & Lift Force Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Drag Force & Lift Force, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice