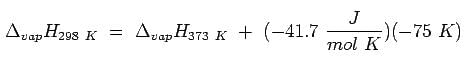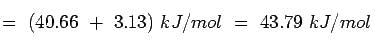Test: Effect of Heat on Matter (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Effect of Heat on Matter (Old NCERT)
Among the following sentences the one that is false about gases is
A cylinder of V litre capacity contains ammonia gas. This cylinder is inverted over another vessel of V litre capacity containing hydrogen chloride at the same temperature and pressure. The pressure in the cylinder after sometime will
The number of elements that exists in gaseous state under normal atmospheric conditions is
The relation between Celsius scale and Fahrenheit scale of measuring temperature is
Which one will have higher value of enthalpy of vaporization:
Choose the characteristic property of gases from the following
Choose the one which is not a characteristic property of gases:
Which of the following sublimes at ordinary temperature:
Thermal energy is directly proportional to:
The conditions necessary for a gas to liquefy are
The temperature in Celsius scale can be converted into Kelvin scale
What happens to density of liquids on increasing temperatures:
What happens to boiling point of a liquid when pressure is increased:
Sublimation involves the direct state change from:
Standard enthalpy of vaporization is taken at:
The standard boiling point of the liquid is
In the process of conversion of a solid to liquid the average distance between the molecules is