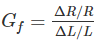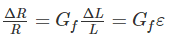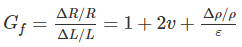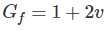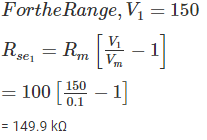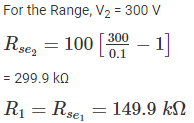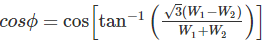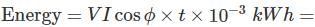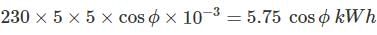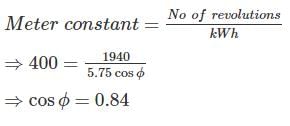Test: Electrical & Electronic Measurements- 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Electrical Engineering SSC JE (Technical) - Test: Electrical & Electronic Measurements- 1
An electrodynamometer type of instruments finds its major use as
An instrument transformer is used to extend the range of-
Perfect reproducibility means the instrument has
A wattmeter reads 25.34 W. The absolute error in measurement is -0.11 W. What is the true value of power:
For wire wound strain gauges, the gauge factor is defined as-
Which one of the following types of instruments does suffer from error due to magnetic hysteresis?
For accuracy of the instrument which is necessary
A null type of instrument as compared to a deflecting type instrument has
A pointer of the instrument once deflected returns to zero position when the current is removed due to:
Two 100V Full scale PMMC type dc voltmeter having figure of merit of 10 kΩ/v and 20 kΩ/v are connected series .The series combination can be used to measure a maximum dc voltage of
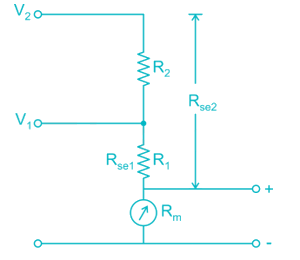
The value of resistances in a potential divider arrangement to convert a basic d Arsonval meter movement with an internal resistance of 100 Ω and a full scale current of 1 mA to a multi range DC voltmeter with ranges 0-150 V and 0-300 V are:
The power in a 3 phase circuit is measured with the help of 2 watt meters. The reading of one of watt meters is positive and that of the others is negative. The magnitude of readings is different. It can be concluded that the power factor of the circuit is
The current and potential coils of a dynamometer type wattmeter were accidentally interchanged while connecting. After energizing the circuit, it was observed that the wattmeter did not show the reading, this could be due to:
Which of the following is not a type of wattmeter?
The power of 6-phase circuit can be measured with a minimum of:
One single phase wattmeter operating on 230 V and 5 A for 5 hours makes 1940 revolutions. Meter constant in revolution is 400. The power factor of the load will be:
A single phase energy meter has a constant of 1200 revolution/kWh. When a load of 200 W is connected, the disc rotates at 4.2 revolutions per min. If the load is on for 10 hours, the meter records an excess of
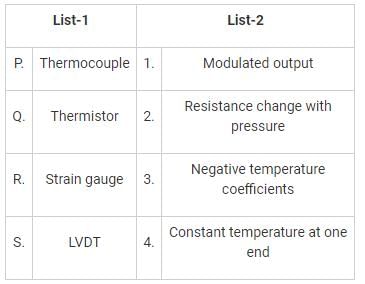
Match List-I (Transducer) with List-2 (Characteristics) and select the correct answer using codes given below the lists:
The purpose of SYNC control in a CRO is to:
Which one of the following is a passive transducer?
|
23 videos|98 docs|42 tests
|