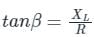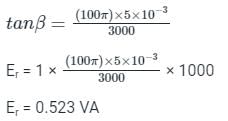Test: Electrodynamometer Type Instruments - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrodynamometer Type Instruments
State TRUE/FALSE for following statements with reference to the dynamometer type instruments:
- The scale is non-uniform.
- Air friction damping is used.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?
A. To avoid stray magnetic field errors
B. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy
C. A soft iron core is placed to direct the flux
A. To avoid stray magnetic field errors
B. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy
C. A soft iron core is placed to direct the flux
A dynamometer wattmeter is rated at 10A and 100V with a full scale reading of 1000 W. The inductance of the voltage circuit is 5mH and its resistance 3000 ohm. Voltage across the current coil is negligible. At 50 Hz and zero power factors, the error in the wattmeter at the VA reading will be:

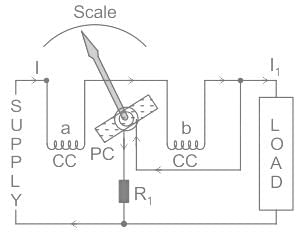
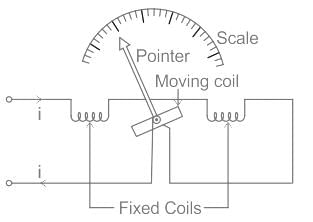
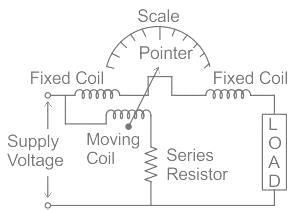
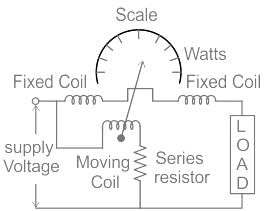
Electro dynamometer type of instruments are enclosed in a casing made up of high permeability material to:
The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is
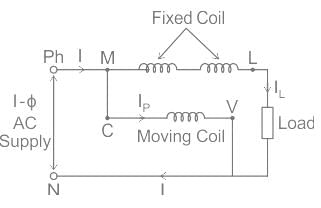
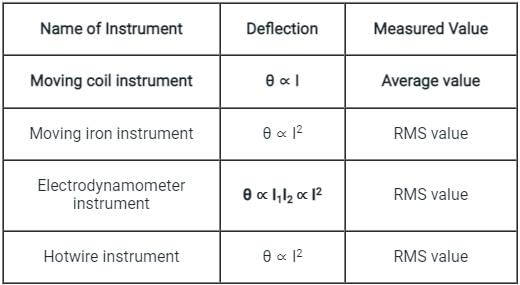
Which of the following principles is utilised in an electrodynamometer type instrument?
The scale of an electrodynamometer usually reads the:
In electrodynamometer movement, the deflection of the pointer is:
Why is Dynamometer type wattmeter is equipped with mirror type scales and knife edge pointers?
In Dynamometer type wattmeter, which type of the coil is split into two parts: