Test: Embryology and Anatomy of Ear - 1 - NEET PG MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Embryology and Anatomy of Ear - 1
True regarding, the marked below is: (MAHE 2007, 2015)

External auditory canal is formed by: (MH 2007, 2015)
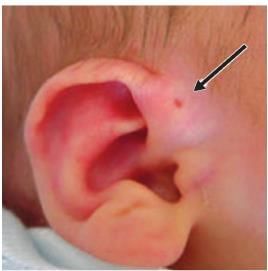
Call Aural fistula is: (JIPMER 2004, 2010)
A newborn presents with bilateral microtia and external auditory canal atresia. Corrective surgery is usually performed at: (AI 2007, 2013)
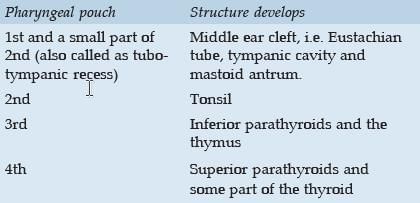
Eustachian tube develops from: (PGI 97, 2011)
The proximal part of Tubotympanic recess leads to the formation of: (MH 2014)
The following structure represents all the three components of the embryonic disc: (TN 98, 2010)
True regarding development of the ear: (PGI 2007, 2012)
Korner’s septum is seen in: (PGI 99, 2013)
All of the following are of the size of adult at birth except: (APPG 06, 2011)
Which of the following attains adult size before birth? (Exam 2013)
Which of the following attains adult size before birth? (AI 2007, 2010)
Inner ear is present in which bone: (PGI 97, 2009)
Inner ear bony labyrinth is: (Karnataka 2006, 2011)
Which of the following is not a pneumatic bone? (AP 2009, 2012)
Crus commune is a part of: (Jharkhand 2006, 2015)
Endolymphatic duct connects which structure: (Delhi 2005, Exam 2017)
Not included in bony labyrinth: (AI 2006, Exam 2017)
The bony cochlea is a coiled tube making ... turns around a bony pyramid called ____: (MH 2003, Exam 2017)
Organ of Corti is situated in: (Kerala 98, Exam 2017)
Foetus starts hearing by what time in intrauterine life: (Exam 2011)
Semicircular canals are stimulated by: (MP 2000, Exam 2013)