Test: Embryology and Anatomy of Ear - 2 - NEET PG MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Embryology and Anatomy of Ear - 2
Horizontal semicircular canal responds to: (UP 2005, Exam 2017)
Angular movements are sensed by: (JIPMER 93, Exam 2013)
Stapes foot plate covers: (AIIMS May 2003, Exam 2017)
Movement of stapes causes vibration in: (Exam 2002, Exam 2017)
Where is electrode kept in cochlear implant? (Exam 2013, AIIMS 2008)
Micro Wick and micro catheter sustained release device are used in (AIIMS 2011)
Site where endolymph is seen: (Kerala 97, Exam 2013)
Fluid, which has high potassium and low sodium content, is: (JIPMER 2003, Exam 2017)
Most potential route for transmission of inner ear infection leading to Meningitis is: (AI 2009, AIIMS 2011)
Infection of CNS spreads in inner ear through: (AIIMS 2010, Exam 2013)
The commonest genetic defect of inner ear causing deafness is: (AIIMS 2010)
Skin over pinna is: (JIPMER 95, Exam 2017)
Length of external auditory canal is: (Exam 2013)
Cartilaginous part of external auditory canal is: (Exam 2017)
Ceruminous glands present in the ear are: (AIIMS May 2005, Exam 2017)
Dehiscence in the external auditory canal cause infection in the parotid gland via: (AIIMS 2004, Exam 2017)
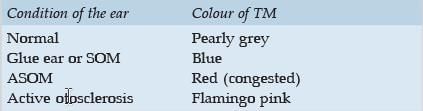
What is the colour of the normal tympanic membrane: (CUPGEE 96, Exam 2017)
Pars Flaccida of the tympanic membrane is also called: (MP 2007, Exam 2013)
The most mobile part of the tympanic membrane: (TN 98, Exam 2017)
Surface area of tympanic membrane: (Manipal 2006, Exam 2013)
The effective vibratory area of the tympanic membrane: (UP 2005, Exam 2017)
Which nerve supplies the tragus? (AIIMS 96, Exam 2017)
Nerve supply for external ear are all except: (MAHE 2007, Exam 2016)