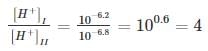Test: Environmental Engineering- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Engineering- 1
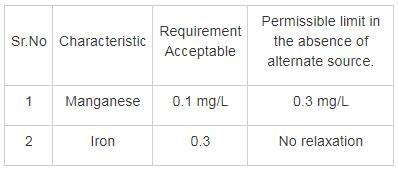
As per IS 10500:2012, the total concentration of manganese (as Mn) and iron (as Fe) for drinking water purpose shall not exceed
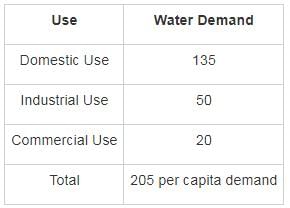
The total domestic water demand for average Indian people is:
Two samples of water form two different sources are collected to measure pH value and it was found to be 6.2 and 6.8. How many times the first sample is more acidic than the second sample?
A water sample analysis produces alkalinity and total hardness of 200 mg/L and 250 mg/L as CaCO3 respectively. The carbonate and non-carbonate hardness (as CaCO3) will respectively be
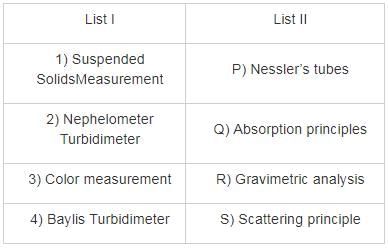
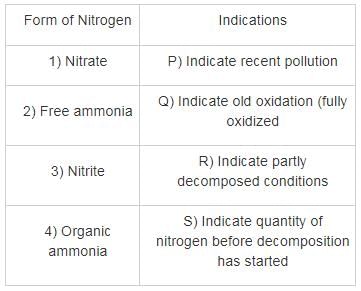
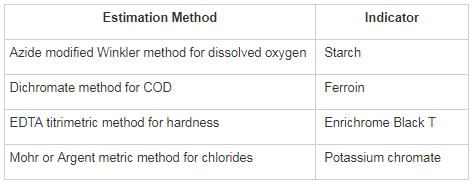
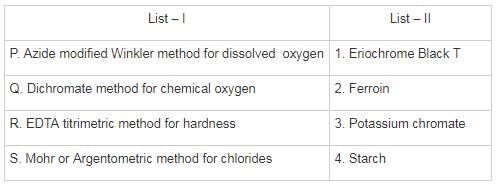
Match List – I (Estimated method) with List – II (Corresponding indicator) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Which one of the following related to domestic potable water quality is CORRECT?
Pollution potential of domestic sewage generated in a town and its industrial sewage can be compared with reference to