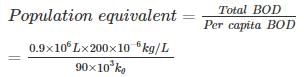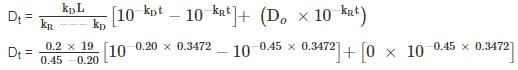Test: Environmental Engineering- 4 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Environmental Engineering- 4
Arrange the given lakes in the descending order of their productivity level
Mesotrophic Lakes
Oligotrophic Lakes
Eutrophic Lakes
The following zones are formed in a polluted river.
(1) zone of clear water
(2) zone of active decomposition
(3) zone of recovery
(4) zone of pollution
The correct sequence in which these zones occur progressively downstream in a polluted river is
In conventional activates sludge process, the mean cell residence time in the aeration tank is–
Deoxygenation constant [kD] at 40o C ----- per day. Assume kD at 20o C is 0.13 per day.
The technique utilized for the disposal of biomedical waste, in which it is in contact with steam under controlled pressure and temperature condition with the end goal to complete sterilization is
The ultimate BOD of wastewater is 300 mg/L and the reaction rate constant (to the base ‘e’) at 20°C is 0.3585/day, then the 5 days BOD at 20oC will be.
The percentage of the relative stability of a test conducted for the determination of relative conductivity at 20°C when the incubation was done for 20 days is _____
A domestic sewage has a BOD of 90 gm per capita. The waste is flowing at a rate of 0.9 MLD having a BOD of 200 mg/l. The population equivalent of the waste is _____.
A large stream has a reoxygenation constant of 0.45 per day and at a point at which organic pollutant is discharged, it is saturated with oxygen at 12 mg/L (Do = 0). Below the outfall, the ultimate demand for oxygen is found to be 19 mg/l and the Deoxygenation Constant is 0.2 per day. Calculate, the D.O at 36 km downstream Assume velocity of the stream to be 1.2 m/s.