Test: First Law Of Thermodynamics - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: First Law Of Thermodynamics - 1
The inlet and the outlet conditions of steam for an adiabatic steam turbine are as indicated in the figure. The notations are as usually followed.
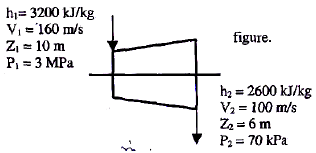
If mass flow rate of steam through the turbine is 20 kg/s the power output of the turbine (in MW) is:
The following four figures have been drawn to represent a fictitious thermodynamic cycle, on the p-v and T-s planes.
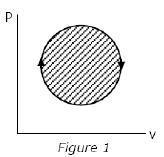
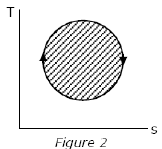
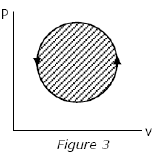
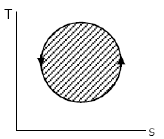
According to the first law of thermodynamics, equal areas are enclosed by
The contents of a well-insulated tank are heated by a resistor of 23 ohm in which 10 A current is flowing. Consider the tank along with its contents as a thermodynamic system. The work done by the system and the heat transfer to the system are positive. The rates of heat (Q), work (W) and change in internal energy (ΔU) during the process in kW are
Which one of the following sets of thermodynamic laws/relations is directly involved in determining the final properties during an adiabatic mixing process?
For a closed system, the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the system is equal to the change in
Which one of the following is correct?
The cyclic integral of for a process is:
A gas is compressed in a cylinder by a movable piston to a volume one-half of its original volume. During the process, 300 kJ heat left the gas and the internal energy remained same. What is the work done on the gas?
Gas contained in a closed system consisting of piston cylinder arrangement is expanded. Work done by the gas during expansion is 50 kJ. Decrease in internal energy of the gas during expansion is 30 kJ. Heat transfer during the process is equal to:
The values of heat transfer and work transfer for four processes of a thermodynamic cycle are given below:
The thermal efficiency and work ratio for the cycle will be respectively.
For a simple closed system of constant composition, the difference between the net heat and work interactions is identifiable as the change in
Change in internal energy in a reversible process occurring in a closed system is equal to the heat transferred if the process occurs at constant:
85 kJ of heat is supplied to a closed system at constant volume. During the next process, the system rejects 90 kJ of heat at constant pressure while 20 kJ of work is done on it. The system is brought to the original state by an adiabatic process. The initial internal energy is 100 kJ. Then what is the quantity of work transfer during the process?
Which of the following is NOT a path function?
When a system is taken from state A to state B along the path A-C-B, 180 kJ of heat flows into the system and it does 130 kJ of work (see figure given):
How much heat will flow into the system along the path A-D-B if the work done by it along the path is 40 kJ?
When a gas is heated at constant pressure, the percentage of the energy supplied, which goes as the internal energy of the gas is:
Assertion (A): If the enthalpy of a closed system decreases by 25 kJ while the system receives 30 kJ of energy by heat transfer, the work done by the system is 55 kJ.
Reason (R): The first law energy balance for a closed system is (notations have their usual meaning)
Which one of the following is the steady flow energy equation for a boiler?
An insulated tank initially contains 0.25 kg of a gas with an internal energy of 200 kJ/kg .Additional gas with an internal energy of 300 kJ/kg and an enthalpy of 400 kJ/kg enters the tank until the total mass of gas contained is 1 kg. What is the final internal energy(in kJ/kg) of the gas in the tank?
Two ideal heat engine cycles are represented in the given figure. Assume VQ = QR, PQ = QS and UP =PR =RT. If the work interaction for the rectangular cycle (WVUR) is 48 Nm, then the work interaction for the other cycle PST is
If a heat engine gives an output of 3 kW when the input is 10,000 J/s, then the thermal efficiency of the engine will be:



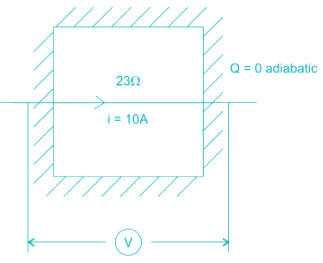 electric work = I2R = 2.3 kW
electric work = I2R = 2.3 kW











