Test: Functions- 3 - CAT MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Functions- 3
If f(x) is an even function, then the graph y = f(x) will be symmetrical about
Find the minimum value of the function fix) = log2 (x2 - 2x + 5).
For what value of x, x2 + 10x + 11 will give the minimum value?
Read the instructions below and solve.
f(x) = f(x – 2) – f(x – 1), x is a natural number
f(1) = 0, f(2) = 1
The value of f(8) is
Read the instructions below and solve.
f(x) = f(x – 2) – f(x – 1), x is a natural number
f(1) = 0, f(2) = 1
What will be the domain of the definition of the function f(x) = 8–xC 5–x for positive values of x?
Ajesh saves Rs 50,000 every year and deposits the money in a bank at compound interest of 10%(compunded annually).What would be his total saving at the end of the 5th year?
Define the following functions:
(a) (a M b) = a – b (b) (a D b) = a + b
(c) (a H b) = (ab) (d) (a P b) = a/b
Q.
Which of the following functions will represent a2 – b2?
Define the following functions:
(a) (a M b) = a – b (b) (a D b) = a + b
(c) (a H b) = (ab) (d) (a P b) = a/b
Q.
What is the value of (3M4H2D4P8M2)?
Define the following functions:
(a) (a M b) = a – b (b) (a D b) = a + b
(c) (a H b) = (ab) (d) (a P b) = a/b
Q.
Which of the four functions defined has the minimum value?
If 0 < a < 1 and 0 < b < 1 and a < b, and if we define a M b = a + b, a D b = a divided by b, and a P b = a multiplied by b, then which of the following expressions has the highest value?
The number of real-valued solutions of the equation 2x+ 2-x = 2 - (x - 2)2 is:



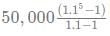 = Rs 3,05,255
= Rs 3,05,255










