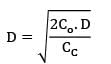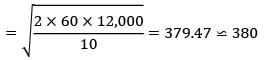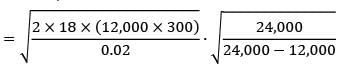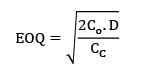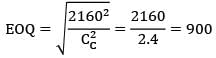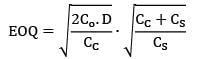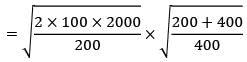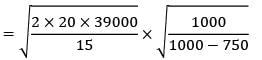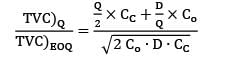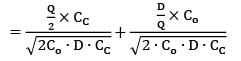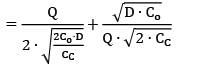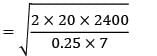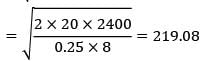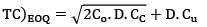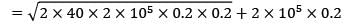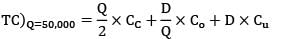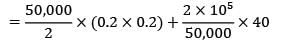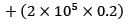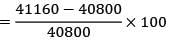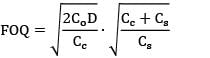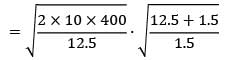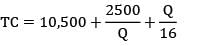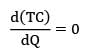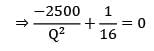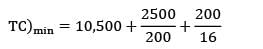Test: Inventory Control Level - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Inventory Control Level - 3
The following data is given for an inventory control system. The annual demand is given as 24,000 units and the safety stock is 200 units. The economic order quantity is 3000 units. If the lead time is 12 days and the number of working days is 300, then the reorder level is __________ units.
Consider the following data Annual usage = 12,000 units, carrying cost is given as 10% of the unit cost. The cost of an item is Rs. 100. The ordering cost per order is given as Rs. 60 Due to some technical reasons the supply is restricted to only 350 units. Find the total annual cost.
The lead time and consumption pattern of a component is as follows:
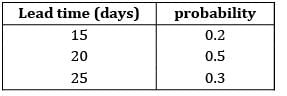
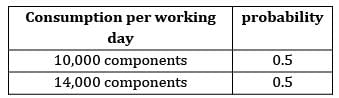
If safety stock = 54,000 units. The ROL is


The annual demand for an item is 4000 units, ordering cost is Rs. 200 per order and inventory holding cost is given as 8 Rs./unit/year. If 4% is offered for a lot of 1200 units then what will be economical ordering quantity. (Assume unit cost of an item is Rs. 40)
The daily demand for a commodity is given as 200 units. A fixed cost of Rs.1000 is incurred every time an order is placed. The carrying cost is given as Rs. 0.02 per unit per day. The minimum annual inventory cost is _____________
A particular item has a carrying cost of Rs. 2.4/unit/year. The total variable cost of inventory at EOQ is given as 2160. The annual demand is 9000 units. If the replacement is instantaneous then find-out the optimal number of order/year.
For lead time and consumption the probabilities are given in the table below
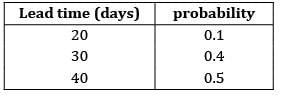
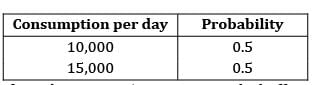
If reorder point is 5,00,000 units. The buffer stock is ______________
A company has an annual demand of 2000 units, ordering cost of Rs. 100/order and a carrying cost of Rs. 200/unit/year. If the shortage costs are estimated to be nearly Rs. 400/unit/year each time the company runs out of stock, then the stock justified by shortage cost is ______________
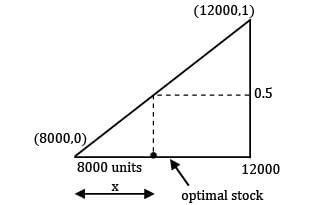
The demand during lead time varies uniformly between 8000 units and 12,000 units. The unit price is given as Rs. 4 and the selling price is Rs. 6. The unsold item has a salvage value of Rs. 2. Determine the optimal level of inventory to stock.
A moulding firm produces and uses 39,000 units annually. The set-up cost is Rs. 20 and production rate per week is 1000 units. If inventory carrying cost is Rs. 15 per unit per annum, the maximum inventory in units is ____________
A company uses 60,000 units per annum of an item, each costing Rs. 120. The ordering cost per order is Rs. 50 and annual inventory carrying costs are 15%. If the company operates 300 days on year, the lead time is given as 10 days and safety stock is 600 units. Find out the re-order level
In an industry, two bin system is used to control inventory for a particular component. The first bin hold 1200 units and the second bin holds 800 units. When first bin gets empty second bin is consumed during the lead time. The annual usage of the component is 40,000 units. The cost to place an order is around Rs. 50, the annual holding cost per unit is Rs. 4. The total variable cost for the two-bin approach is __________
If the ratio of total incremental cost for a quantity Q to total incremental cost for EOQ quantity is 2, then the ratio of quantity Q to EOQ is _________
Find the economic order quantity for a product of which the price breaks are as follows
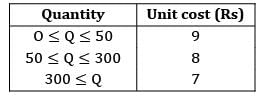
The monthly demand for the product is 200 units. The cost of holding is 25% of the unit cost and the ordering cost is Rs. 20/order.
The monthly consumption of an item is 500 units. The price per unit is Rs. 25. The inventory carrying cost is 16% of item cost and ordering cost is Rs. 50 per order. For an economic order quantity model, determine the Re-order quantity
A company has to manufacture 2,00,000 brackets in a year. It orders raw materials for the brackets in lots of 50,000 units from a vendor. It costs Rs. 40 to place an order, inventory carrying costs are 20% of the item cost/yr which is Rs. 0.2/unit. Calculate the variation of cost (in %) in their order quantity from optimal?
Consider an item with the following characteristics.
Annual demand = 400 /yr
Unit cost = Rs. 25
Inventory carrying cost = 20 % of unit cost
Cost of one procurement = Rs. 10
Shortage cost = Rs. 1.5/Unit-year
Based on the above data the time duration between two consecutive orders will be __________ months.
The total cost is represented with the following equation, TC = 10,500 +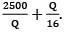 Then TC)min is __________
Then TC)min is __________