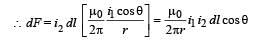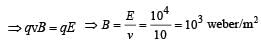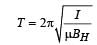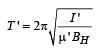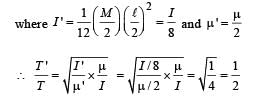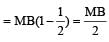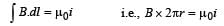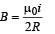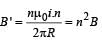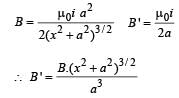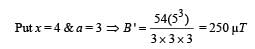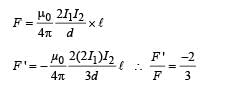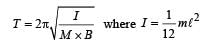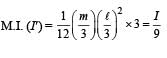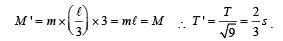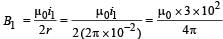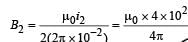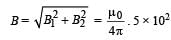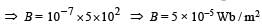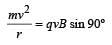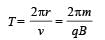Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Moving Charges & Magnetism - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Moving Charges & Magnetism
Advanced countries are making use of powerful electromagnets to move trains at very high speed. These trains are called maglev trains (abbreviated from magnetic levitation). These trains float on a guideway and do not run on steel rail tracks.Instead of using a engine based on fossil fuels, they make use of magnetic field forces. The magnetized coils are arranged in the guide way which repels the strong magnets placed in the train's under carriage. This helps train move over the guideway , a technic called electro-dynamic suspension. When current passes in the coils of guideway , a typical magnetic field is set up between the undercarriage of train and guideway which pushes and pull the train along the guideway depending on the requirement.The lack of friction and its aerodynamic style allows the train to more at very high speed.
Q.1. The levitation of the train is due to
Advanced countries are making use of powerful electromagnets to move trains at very high speed. These trains are called maglev trains (abbreviated from magnetic levitation). These trains float on a guideway and do not run on steel rail tracks.Instead of using a engine based on fossil fuels, they make use of magnetic field forces. The magnetized coils are arranged in the guide way which repels the strong magnets placed in the train's under carriage. This helps train move over the guideway , a technic called electro-dynamic suspension. When current passes in the coils of guideway , a typical magnetic field is set up between the undercarriage of train and guideway which pushes and pull the train along the guideway depending on the requirement.The lack of friction and its aerodynamic style allows the train to more at very high speed.
Q.2. The disadvantage of maglev trains is that
Advanced countries are making use of powerful electromagnets to move trains at very high speed. These trains are called maglev trains (abbreviated from magnetic levitation). These trains float on a guideway and do not run on steel rail tracks.Instead of using a engine based on fossil fuels, they make use of magnetic field forces. The magnetized coils are arranged in the guide way which repels the strong magnets placed in the train's under carriage. This helps train move over the guideway , a technic called electro-dynamic suspension. When current passes in the coils of guideway , a typical magnetic field is set up between the undercarriage of train and guideway which pushes and pull the train along the guideway depending on the requirement.The lack of friction and its aerodynamic style allows the train to more at very high speed.
Q.3. The force which makes maglev move
The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wires (numbered 1 and 2) all in the plane of the paper. The distance of each wire from the centre of the loop is d. The loop and the wire are carrying the same current I.The current in the loop is in the counterclockwise direction if seen from above.
(q) The magnetic fields (B) at P due to the currents in the wires are in opposite directions.
(r) There is no magnetic field at P.
(s) The wires repel each other.
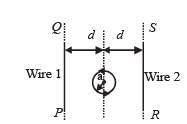
Q.4.When d ≈ a but wires are not touching the loop, it is found that the net magnetic field on the axis of the loop is zero at a height h above the loop. In that case
The figure shows a circular loop of radius a with two long parallel wires (numbered 1 and 2) all in the plane of the paper. The distance of each wire from the centre of the loop is d. The loop and the wire are carrying the same current I.The current in the loop is in the counterclockwise direction if seen from above.
(q) The magnetic fields (B) at P due to the currents in the wires are in opposite directions.
(r) There is no magnetic field at P.
(s) The wires repel each other.

Q.5. Consider d >> a, and the loop is rotated about its diameter parallel to the wires by 30° from the position shown in the figure. If the currents in the wires are in the opposite directions, the torque on the loop at its new position will be (assume that the net field due to the wires is constant over the loop).
In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along the positive x-direction, as shown in the figure. The length, width and thickness of the strip are l, w and d, respectively.A uniform magnetic field  is applied on the strip along the positive y-direction. Due to this, the charge carriers experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal and opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z-direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross-section of the strip and carried by electrons.
is applied on the strip along the positive y-direction. Due to this, the charge carriers experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal and opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z-direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross-section of the strip and carried by electrons.
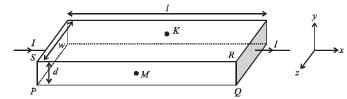
Q.6. Consider two different metallic strips (1 and 2) of the same material. Their lengths are the same, widths are w1 and w2 and thicknesses are d1 and d2 respectively. Two points K and M are symmetrically located on the opposite faces parallel to the x-y plane (see figure). V1 and V2 are the potential differences between K and M in strips 1 and 2, respectively. Then, for a given current I flowing through them in a given magnetic field strength B, the correct statement(s) is(are)
In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current I flows along the positive x-direction, as shown in the figure. The length, width and thickness of the strip are l, w and d, respectively.A uniform magnetic field  is applied on the strip along the positive y-direction. Due to this, the charge carriers experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal and opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z-direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross-section of the strip and carried by electrons.
is applied on the strip along the positive y-direction. Due to this, the charge carriers experience a net deflection along the z-direction. This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface PQRS and appearance of equal and opposite charges on the face opposite to PQRS. A potential difference along the z-direction is thus developed. Charge accumulation continues until the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross-section of the strip and carried by electrons.

Q.7. Consider two different metallic strips (1 and 2) of same dimensions (length l, width w and thickness d) with carrier densities n1 and n2, respectively. Strip 1 is placed in magnetic field B1 and strip 2 is placed in magnetic field B2, both along positive y-directions. Then V1 and V2 are the potential differences developed between K and M in strips 1 and 2, respectively. Assuming that the current I is the same for both the strips, the correct option(s) is(are)
Statement-1 : The sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer is increased by placing a suitable magnetic material as a core inside the coil. and Statement-2 : Soft iron has a high magnetic permeability and cannot be easily magnetized or demagnetized.
If in a circular coil A of radius R, current I is flowing and in another coil B of radius 2R a current 2I is flowing, then the ratio of the magnetic fields BA and BB, produced by them will be
If an electron and a proton having same momenta enter perpendicular to a magnetic field, then
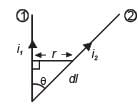
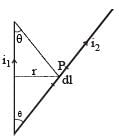
Wires 1 and 2 carrying currents i1 and i2 respectively are inclined at an angle θ to each other. What is the force on a small element dl of wire 2 at a distance of r from wire 1 (as shown in figure) due to the magnetic field of wire 1?
The time period of a charged particle undergoing a circular motion in a uniform magnetic field is independent of its
A particle of mass M and charge Q moving with velocity 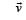 describe a circular path of radius R when subjected to a uniform transverse magnetic field of induction B. The work done by the field when the particle completes one full circle is
describe a circular path of radius R when subjected to a uniform transverse magnetic field of induction B. The work done by the field when the particle completes one full circle is
A particle of charge - 16 *10 -18 coulomb moving with velocity 10ms-1 along the x-axis enters a region where a magnetic field of induction B is along the y-axis, and an electric field of magnitude 10 4 V / m is along the negative z-axis. If the charged particle continues moving along the x-axis, the magnitude of B is
A thin rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely in the same field. If its period of oscillation is T ' , the ratio T '/T is
A magnetic needle lying parallel to a magnetic field requiers W units of work to turn it through 600 . The torque needed to maintain the needle in this position will be
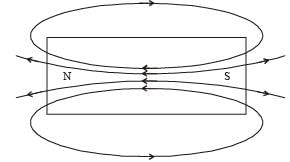
The magnetic lines of force inside a bar magnet
Curie temperature is the temperature above which
A current i ampere flows along an infinitely long straight thin walled tube, then the magnetic induction at any point inside the tube is
A long wire carries a steady current. It is bent into a circle of one turn and the magnetic field at the centre of the coil is B. It is then bent into a circular loop of n turns. The magnetic field at the centre of the coil will be
The magnetic field due to a current carrying circular loop of radius 3 cm at a point on the axis at a distance of 4 cm from the centre is 54 μT. What will be its value at the centre of loop?
Two long conductors, separated by a distance d carry current I1 and I2 in the same direction. They exert a force F on each other. Now the current in one of them is increased to two times and its direction is reversed. The distance is also increased to 3d. The new value of the force between them is
The length of a magnet is large compared to its width and breadth. The time period of its oscillation in a vibration magnetometer is 2s. The magnet is cut along its length into three equal parts and these parts are then placed on each other with their like poles together. The time period of this combination will be
The materials suitable for making electromagnets should have
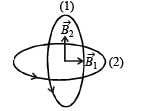
Two concentric coils each of radius equal to 2 π cm are placed at right angles to each other. 3 ampere and 4 ampere are the currents flowing in each coil respectively. The magnetic induction in Weber / m2 at the centre of the coils will be
A charged particle of mass m and charge q travels on a circular path of radius r that is perpendicular to a magnetic field B. The time taken by the particle to complete one revolution is
A magnetic needle is kept in a non-uniform magnetic field. It experiences
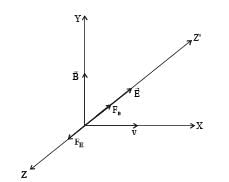
A uniform electric field and a uniform magnetic field are acting along the same direction in a certain region. If an electron is projected along the direction of the fields with a certain velocity then
Needles N1, N2 and N3 are made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. A magnet when brought close to them will
In a region, steady and uniform electric and magnetic fields are present. These two fields are parallel to each other. A charged particle is released from rest in this region. The path of the particle will be a



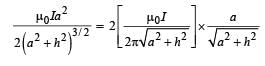
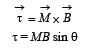
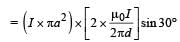
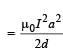

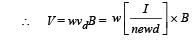
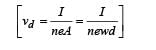
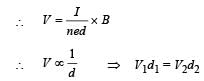
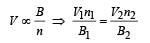
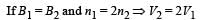
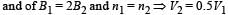
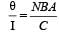 . If B increases, θ/I
. If B increases, θ/I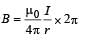
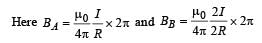
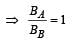
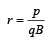
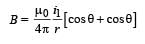
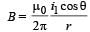 (directed perpendicular to the plane of paper, inwards)
(directed perpendicular to the plane of paper, inwards)