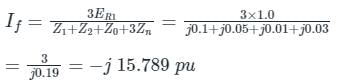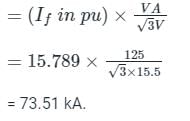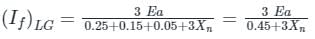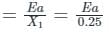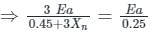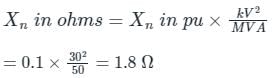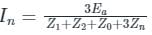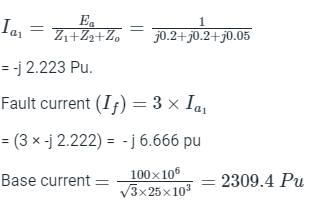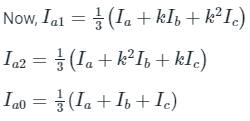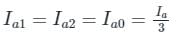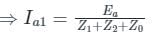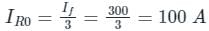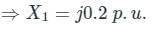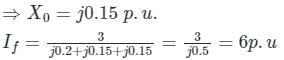Test: Line to Ground Fault - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Line to Ground Fault
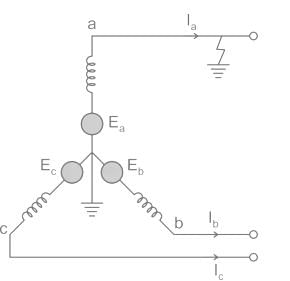
For a fault at terminals of a synchronous generator, the fault current is maximum for a
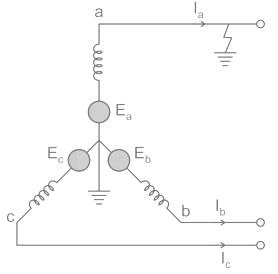
The positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of a 125 MVA, three-phase, 15.5 kV, star-grounded, 50 Hz generator are j0.1 pu, j0.05 pu and j0.01 pu respectively on the machine rating base. The machine is unloaded and working at the rated terminal voltage. If the grounding impedance of the generator is j0.01 pu, then the magnitude of fault current for a b-phase to ground fault (in kA) is __________ (up to 2 decimal places).
A 30 kV, 50 Hz, 50 MVA generator has the positive, negative, and zero sequence reactance’s of 0.25 pu, 0.15 pu, and 0.05 pu, respectively. The neutral of the generator is grounded with a reactance so that the fault current for a bolted LG fault and that of a bolted three-phase fault at the generator terminal are equal. The value of grounding reactance in ohms (round off to one decimal
A three phase, 100 MVA, 25kV generator has solidly grounded neutral. The positive, negative, and the zero sequence reactances of the generator are 0.2 pu, 0.2 pu, and 0.05 pu, respectively, at the machine base quantities. If a bolted single phase to ground fault occurs at the terminal of the unloaded generator, the fault current in amperes immediately after the fault is________.
What will the zero-sequence current when line to ground fault occurs and the current in faulted phase is 300 A?
The zero sequence current of generator for line to ground fault is j2.4 pu. Then current through the neutral during the fault is
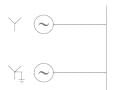
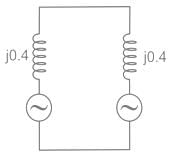
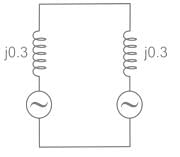
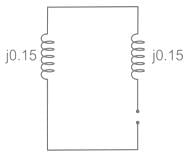
Two identical unloaded generators are connected in parallel as shown in the figure. Both the generators are having positive, negative and zero sequence impedances of j0.4 p.u., j0.3 p.u.and j0.15 p.u., respectively. If the pre-fault voltage is 1 p.u., for a line-to-ground (L-G) fault at the terminals of the generators, the fault current, in p.u., is ___________.