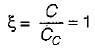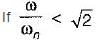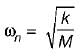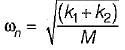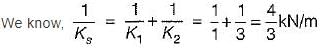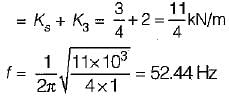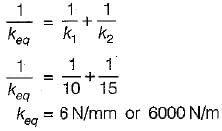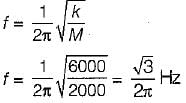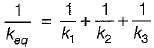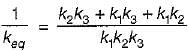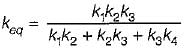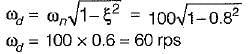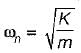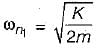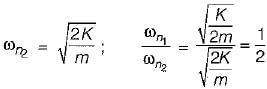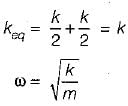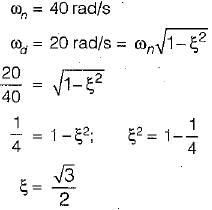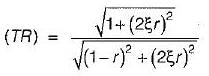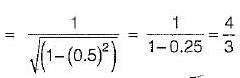Test: Linear Vibration Analysis - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Linear Vibration Analysis - 3
The ratio of the actual damping coefficient to the critical damping coefficient is called
If the damping factor for a vibrating system is unity then the system is
In vibration isolation system, if 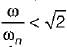 the for all values of damping factor, the transmissibility will be
the for all values of damping factor, the transmissibility will be
The ratio of maximum displacement of forced vibration to the deflection due to the static force is known as
The normal speed of rotation of a shaft is chosen to be
In a multi-rotor system of torsional vibration maximum number of nodes that can occur is
A shaft carrying three rotors at ends will have following number of nodes
During torsional vibration of a shaft, the node is characterized by the
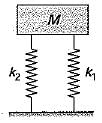
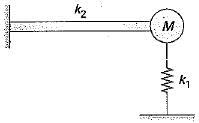
A cantilever beam of negligible weight is carrying a mass M at its free end, and is also resting on an elastic support of stiffness k1, as shown in the figure below.
If k2 represents the bending stiffness of the beam, the natural frequency (rad/s) of the system is
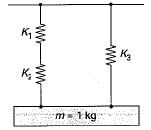
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of 3 springs as shown in figure. The spring constant K1, K2 and K3 are respectively 1 kN/m, 3 kN/m and 2 kN/m. The natural frequency of the system is approximately
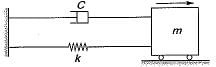
The figure shows a critically damped spring-mass system undergoing single degree of freedom vibrations. If m = 5 kg and k = 20 N/m, the value of viscous damping coefficient is
Two spring of equal length but having stiffness of 10 N/mm and 15 N/mm support a mass of 2 tonnes in series. Find the frequency of vibration
Three spring of stiffness k1, k2 and k3 are connected in series. The stiffness of a single spring equivalent to these three springs would be equal to
Natural frequency of undamped free vibration is 100 rps and damping is provided with damping factor is 0.8 then what is the frequency of damped vibration
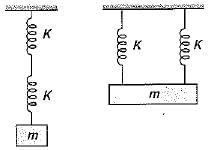
Two identical springs of constant K are connected in series and parallel as shown in the figure. A mass m is suspended from them. The ratio of their frequencies of oscillations will be
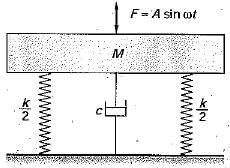
The given figure show vibrations of a mass ‘M’ isolated by means of springs and a damper. If an external force ‘F (= A sin ωt) acts on the mass and the damper is not used, then
A spring-mass suspension has a natural frequency of 40 rad/s. What is the damping ratio required if it is desired to reduce this frequency to 20 rad/s by adding a damper to it?
A vibrating machine is isolated from the floor using springs, if the ratio of excitation frequency of vibration of machine to the natural frequency of the isolation system is equal to 0.5, the transmissibility ratio of isolation is