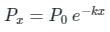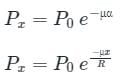Test: Loss of Prestress - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test RCC & Prestressed Concrete - Test: Loss of Prestress
A post-tensioned prestressed concrete beam is stressed by three cables, each with c/s area of 50 mm2 with an initial stress of 900 MPa. If all three cables are straight and located at an eccentricity of 50 mm, consider modular ratio (m) = 6 and stress in concrete at the level of steel (fc) = 5 MPa, than what will be the loss in stress in cables due to elastic shortening if all vales are simultaneously tensioning and anchoring?
In case of curved ducts, the loss of prestress depends upon the radius of curvature (R) of the duct and the coefficient of friction (μ) between duct surface and the tendon. The tension at any point of the cable distance 'x' from the end is given by ________.
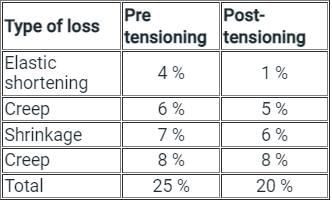
A post tensioned prestressed concrete beam is tensioned successively by 4 cables of equal area and equal stress. The percentage loss in each cable is found to be 6%, 4%, 2% and 0% respectively. What will be the total percentage loss in prestressing force?
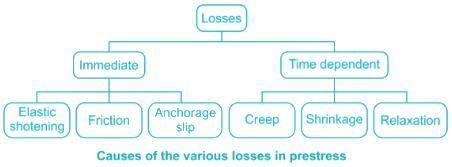
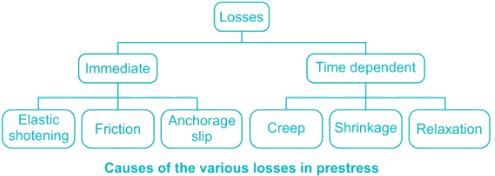
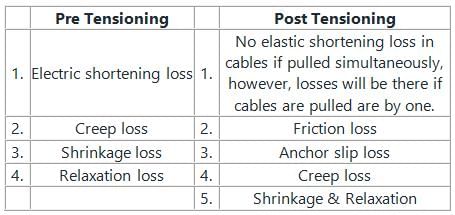
The following loss does not occur in Pre-tensioning of concrete
The loss in pre-stress in pre-tensioning system is primarily due to
Loss of stress due to relaxation of steel is influenced by
|
13 videos|42 docs|34 tests
|