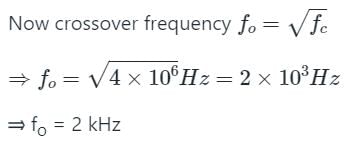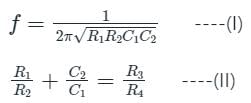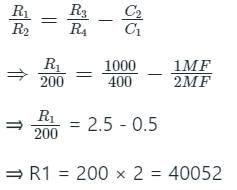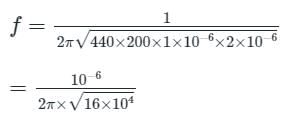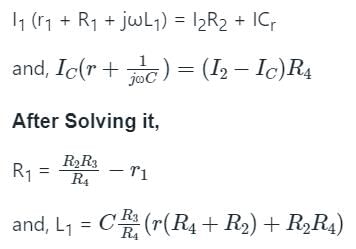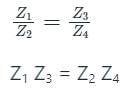Test: Measurement of Frequency - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Measurement of Frequency
While using a frequency counter for measuring frequency, two modes of measurement are possible. I) Period mode ii) Frequency mode. There is a ‘cross-over frequency’ below which the period mode is preferred. Assuming the crystal oscillator frequency to be 4 MHz the cross-over frequency is given by
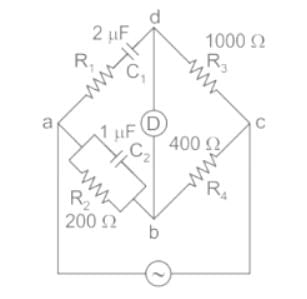
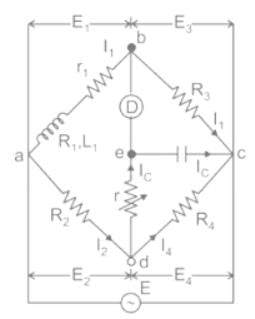
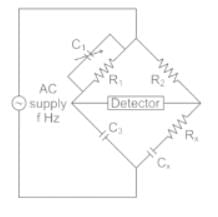
The arms of a four-arm bridge abcd, supplied with sinusoidal voltage, have the following values :
Arm ab: A resistance of 200 Ω in parallel with a capacitance of 1 μF
Arm bc: 400 Ω resistance
Arm cd: 1000 Ω resistance
Arm da: A resistance R2 in series with a 2 μF capacitance
What are the values of R2 and the frequency respectively at which the bridge will balance?
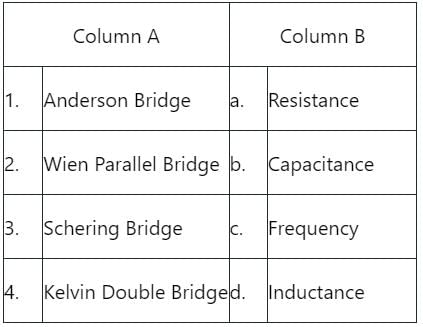
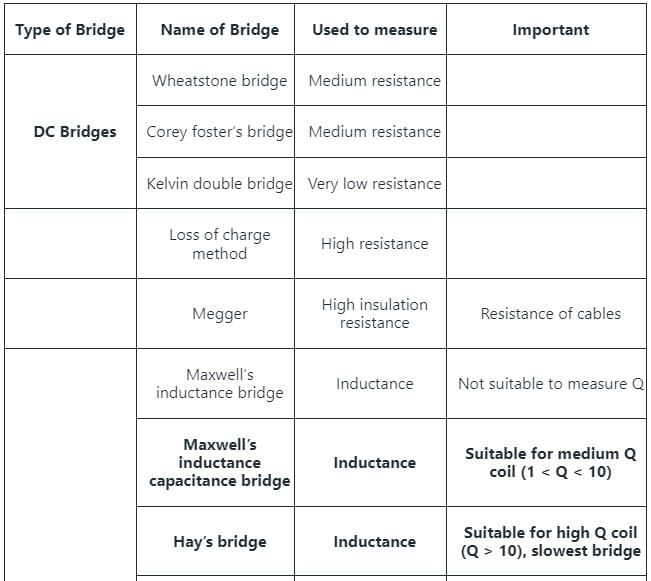
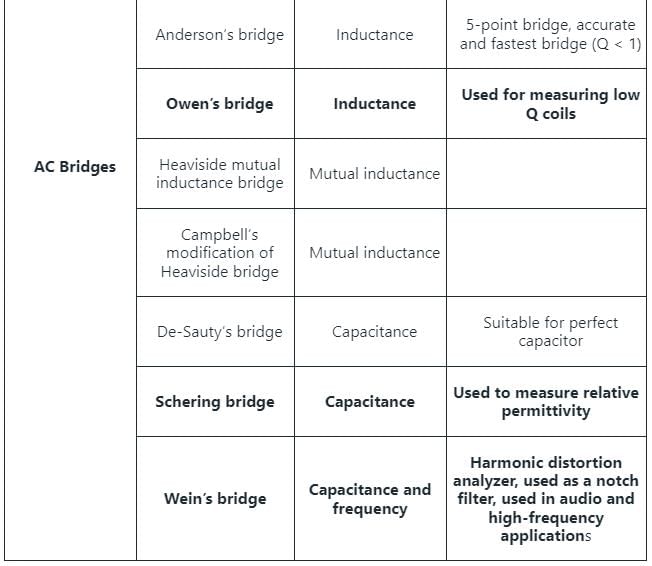
Which method requires a standard capacitor in terms of which the selfinductance is expressed?
In a vibrating reed type frequency meter, the reed which will vibrate the most is the one whose natural frequency is equal to
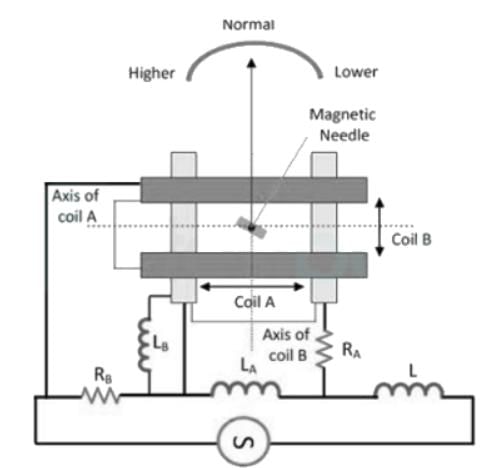
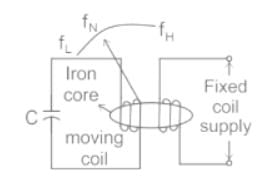
Working principle of Weston type frequency meter is based on which of the following principles?
In which type of frequency meter, the frequency is found when the torque’ in the moving coil becomes zero?
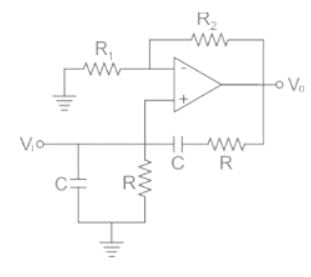
Frequency of oscillation of Weinbridge oscillator is given as:
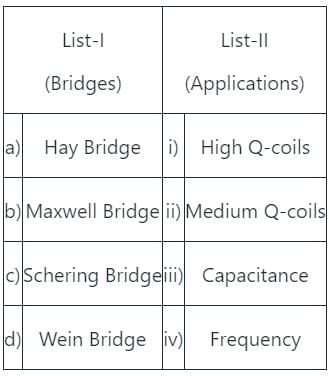
Which of the following bridges is used to measure power factor?
State TRUE/FALSE for the following statements:
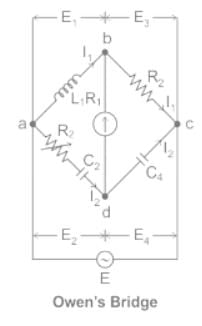
1. Owen’s bridge needs a variable standard capacitor.
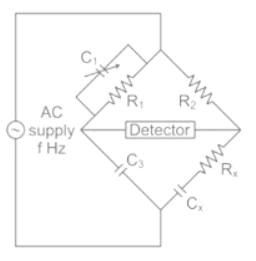
2. Schering bridge can be used for measurement of dielectric loss.