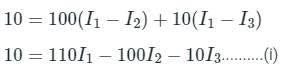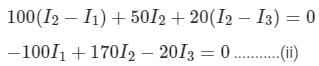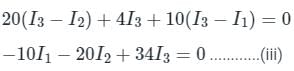Test: Measurement of Resistance - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Measurement of Resistance - 1
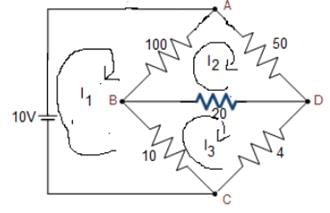
The resistances of the four arms of a Wheatstone bridge are as follows: AB = 100, BC = 10, CD = 4, DA = 50 ohms. A 20-ohm resistance galvanometer is connected between BD. If there is a potential difference of 10 V across the AC, then find the value of the current flowing through the galvanometer.
Consider the following in context of creeping in energy meter and identify the correct option.
P: The primary reason of creeping is under-compensation for friction.
Q: Creeping may be because of excessive voltage and vibrations.
______ eliminates errors due to contacts and ______ in bridge measuring instruments.
The electrical power to a megger is provided by
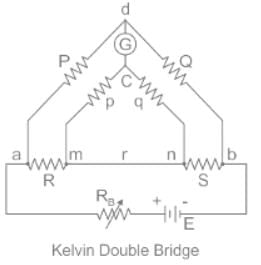
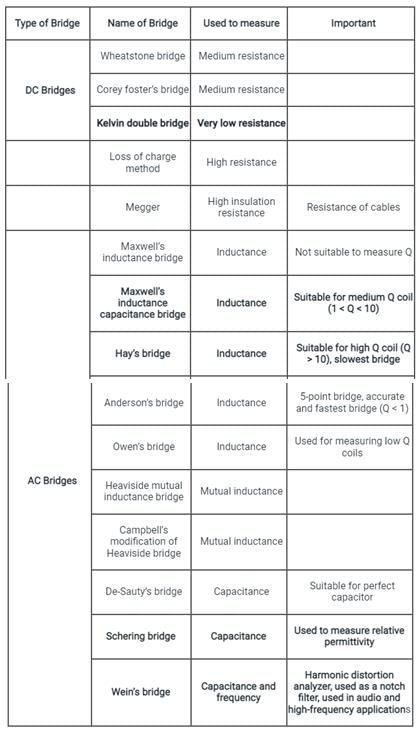
Kelvin double bridge is best suited for the measurement of
A megger is an instrument that gives the reading in:
The operation of a Megger is based on which of the following?
The test used to locate high resistance faults in low resistance conductor circuit is:
In a megger, controlling torque is provided by
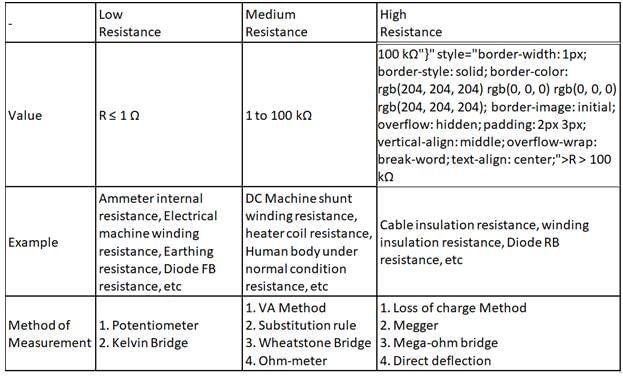
For the measurement of high resistances following methods are used:
1. Loss of Charge Method
2. Direct Deflection Method
3. Substitution Method
Which of the following is/are correct?