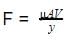Test: Measurement of Viscosity - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation - Test: Measurement of Viscosity
Two parallel plates separated by 1.45 cm are filled with a liquid with a viscosity of 3.6 × 10−2 Pa·s. What is the force acting on 1m2 of the plate, if the other plate is given a velocity of 2.3 m/s?
In a falling-ball viscometer, the ball attains terminal velocities of 0.01 m/s for oil A and 0.002 m/s for oil B. Assuming the oils have the same density and oil A has a kinematic viscosity of 5 x 10– 3 m2/s, the kinematic viscosity of oil B in m2/s is
A viscous damper consists of a sliding piston and a cylinder filled with the oil of kinematic viscosity 5 × 10– 5 m2/s. A damping force of 20 N is applied on the piston and the steady-state velocity reached is 10 mm/s. The damping coefficient of the damper is
A capillary viscometer, with known dimensions, is used for measuring dynamic viscosity of the oil. In order to obtain viscosity, it is necessary and sufficient if one measure
Which of the following represents the slow-motion of layers of fluid in one direction?
If shear stress is equally proportional to velocity gradient, fluid is called as
Which of the following represents relation for kinematic viscosity?
What happens to the viscosity of liquid and gas when the temperature is increased?
Which of the following is not converting viscosity to pressure?
|
26 videos|28 docs|29 tests
|