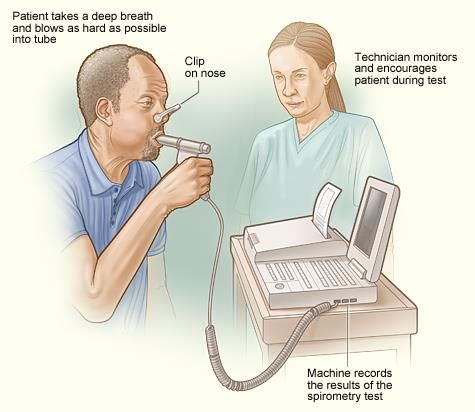
NEET Exam > NEET Tests > Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - NEET MCQ
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - NEET MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3)
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) questions and answers have been prepared
according to the NEET exam syllabus.The Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) below.
Solutions of Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) questions in English are available as part of our course for NEET & Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) solutions in
Hindi for NEET course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for NEET preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for NEET Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 1
In breathing movements, the air volume can be estimated by:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 2
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 3
The vital capacity of the lungs includes:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 4
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 5
A person breathes in some volume of air by forced inspiration after having a forced expiration.
This quantity of air taken in is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 5
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 6
Which of the following statement is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 6
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 7
In humans, which among these is not a step in respiration?
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 7
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 8
The amount of volume of air which can be inspired/expired normally is called:
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 9
Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 10
Mammalian erythrocytes have short life span due to absence of
Detailed Solution for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) - Question 10
Information about Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3) solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Mechanism of Breathing (August 3), EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF