Test: Mendeleev's periodic table, Modern periodic table - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Mendeleev's periodic table, Modern periodic table
Arrange the following in increasing order of ionic radii? 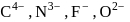
The cause of periodicity of properties of elements is due to the repetition of similar:
Tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electron towards itself is called:
Which one of the following is correct order of second ionisation potential of 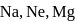 and
and 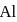 ?
?
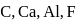 and
and 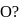
The maximum covalency and highest oxidation state possible for an element with Z = 13 are respectively.
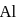 is
is 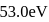 atom
atom 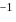 and the sum of first two ionization energies of
and the sum of first two ionization energies of 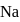 is
is 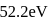 atom
atom 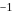 . Out of Al(III) and
. Out of Al(III) and 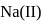
The correct order of decreasing electronegatıvity values among the elements I-beryllium, II-oxygen, III-nitrogen and IV-magnesium is
Correct order of first IP among following elements Be,B,C,N,O is
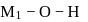 and
and 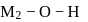 are prepared in two different beakers. If, the electronegativity of
are prepared in two different beakers. If, the electronegativity of 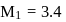 ,
, 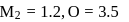 and
and 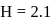 then the nature of two solutions will be respectively :
then the nature of two solutions will be respectively :
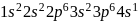 forms
forms
The correct order of first ionisation enthalpy of group-13 elements is
If the ionization enthalpy and electron gain enthalpy of an element are 275 and  respectively, then the electronegativity of the elementon the Pauling scale is:
respectively, then the electronegativity of the elementon the Pauling scale is:
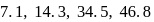 and
and 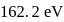 respectively. The element is likely to be:
respectively. The element is likely to be:



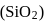 .
.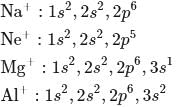
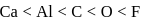
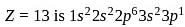
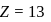 is 6.
is 6.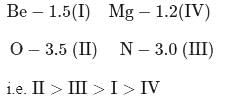

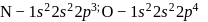
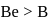 . Further IP of
. Further IP of 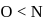 because atoms with fully or partly filled orbitals are most stable and hence have high ionisation energy.
because atoms with fully or partly filled orbitals are most stable and hence have high ionisation energy.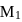 and
and 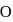 is
is 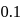 , which indicates
, which indicates 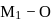 bond will be covalent, since
bond will be covalent, since 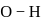 bond having more ionic character thus bond will break and
bond having more ionic character thus bond will break and 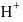 ions gets release and acidic solution is formed and whereas difference between electronegativity of
ions gets release and acidic solution is formed and whereas difference between electronegativity of 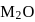 is
is 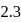 , thus,
, thus, 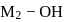 bond will break. Hence, solution will be basic in nature.
bond will break. Hence, solution will be basic in nature.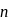 increases, the nuclear attraction over the outermost shell decreases, therefore removal of an electron will be easier.
increases, the nuclear attraction over the outermost shell decreases, therefore removal of an electron will be easier. E.A.
E.A. 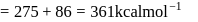
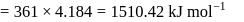
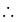 Electronegativity
Electronegativity 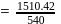
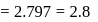
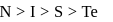 .
.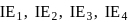 and
and 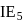 of an element are
of an element are 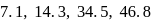 and
and 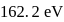 respectively. Therefore, We can see that there is a regular very close increment of ionization energy till the fourth ionization energy. After the fourth ionization energy, there is a sudden high jump in energy. It confirms that after losing four electrons, that element will achieve the noble gas configuration or stable configuration.
respectively. Therefore, We can see that there is a regular very close increment of ionization energy till the fourth ionization energy. After the fourth ionization energy, there is a sudden high jump in energy. It confirms that after losing four electrons, that element will achieve the noble gas configuration or stable configuration.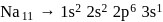
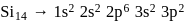
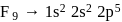
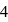 and it is most likely to be silicon.
and it is most likely to be silicon.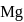 has only two electrons in the 3 s-orbital and hence its
has only two electrons in the 3 s-orbital and hence its 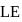 . is lowest, i.e. it has the maximum tendency to from di-positive ions.
. is lowest, i.e. it has the maximum tendency to from di-positive ions.










