Test: Moore Machine - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Moore Machine
For a give Moore Machine, Given Input=’101010’, thus the output would be of length:
Statement 1: Null string is accepted in Moore Machine.
Statement 2: There are more than 5-Tuples in the definition of Moore Machine.
Choose the correct option:
The total number of states and transitions required to form a moore machine that will produce residue mod 3.
The Finite state machine described by the following state diagram with A as starting state, where an arc label is x / y and x stands for 1-bit input and y stands for 2- bit output
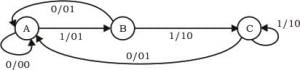
What is the output for the given language?
Language: A set of strings over ∑= {a, b} is taken as input and it prints 1 as an output “for every occurrence of a, b as its substring. (INPUT: abaaab)
The O/P of Moore machine can be represented in the following format:



















