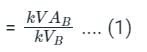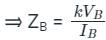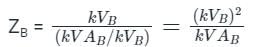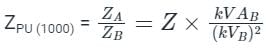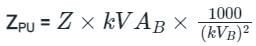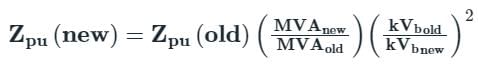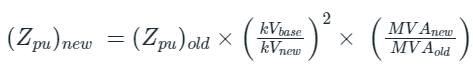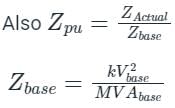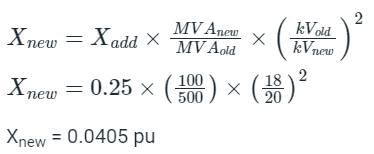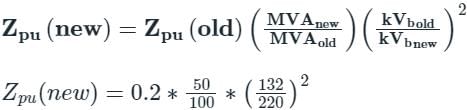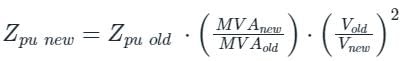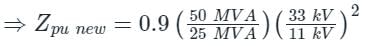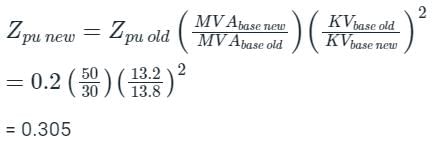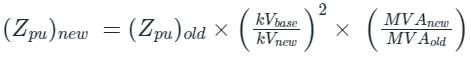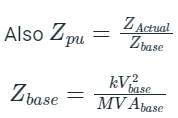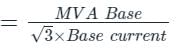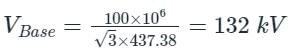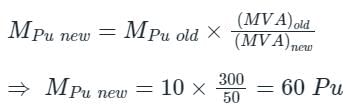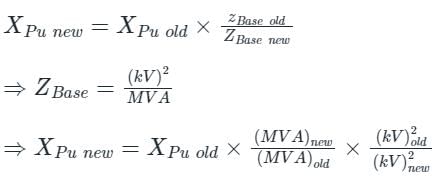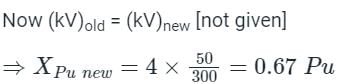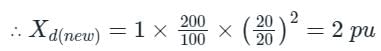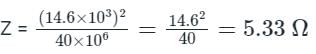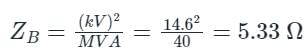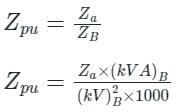Test: Per Unit System - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Per Unit System
The per unit impedance of a circuit element is x. If the base kV and base MVA are doubled, then the new value of the per unit impedance of the circuit element is
The reactance of a generator designated ‘x’ is given as 0.25 pu based on the generator’s name plate rating of 18 kV, 500 MVA. If the base for calculations is changed to 20 kV, 100 MVA, the generator reactance X on new base will be - (in pu)
On a base of 132 kV, 100 MVA, a transmission line has 0.2 per unit impedance. On a base of 220 kV, 50 MVA, it will have a per unit impedance of:
A 50 Hz synchronous generator is initially connected to a long lossless transmission line which is open circuited at the receiving end. With the field voltage held constant, the generator is disconnected from the transmission line. Which of the following may be said about the steady state terminal voltage and field current of the generator?

A 25 MVA, 33 kV transformer has a pu impedance of 0.9. The pu impedance at a new base 50 MVA at 11 kV would be
The per unit impedance of an alternator corresponding to base values 13.2 kV and 30 MVA is 0.2 p.u. The pu value of the impedance for base value 13.8 kV and 50 MVA in pu will be
A three phase star-connected load is drawing power at a voltage of 0.9 pu and 0.8 power factor lagging. The three phase base power and base current are 100 MVA and 437.38 A respectively. The line-to-line load voltage in kV is _______. (Important - Enter only the numerical value in the answer)
The pu parameters for a 300 MVA machine on its own base are inertia M = 10 pu and reactance X = 4 pu. The pu values of inertia and reactance on 50 MVA common base, respectively, will be:
A 500 MVA, 11KV synchronous generator has 0.2 p.u. synchronous reactance. The p.u. synchronous reactance on the base values of 100 MVA and 22 KV is
Calculate the per-unit synchronous reactance on the base value of 200 MVA and 20 kV when a 100 MVA with 20 kV synchronous generator has 1pu synchronous reactance.
A synchronous generator is rated at 40 MVA, 14.6 kV and 50 Hz. The base impedance of the generator will be
Which of the following depicts Per-unit value of a quantity?