Test: Powder Metallurgy - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Powder Metallurgy - 1
The products made by powder metallurgy process are very strong in
In solid-state bonding during sintering of a powder-metal green compact, the linear shrinkage is 5%. If the desired sintered density is 92% of the theoretical density of the metal, what should be the density of the green compact? Ignore the small changes in mass that occur during sintering.
Which of the following P/M products is made by impregnation?
Various additives, such as binders as in sand molds, are used to develop sufficient green strength and facilitate sintering in
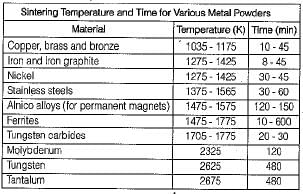
he powder-metallurgy-operation consists of the following steps:
1. Blending
2. Powder production
3. Compaction
4. Finishing operations
5. Sintering
Arrange the above in operational seuquence:
Which one of the following cutting tool bits are made by powder metallurgy processes?


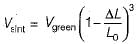
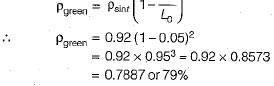

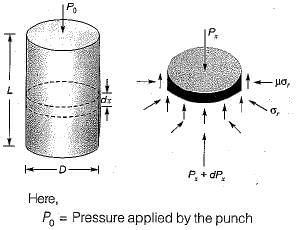
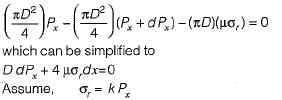
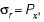 signifying a state of hydrostatic pressure.
signifying a state of hydrostatic pressure.
















