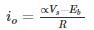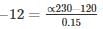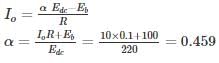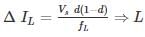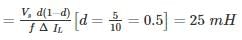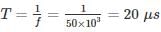Test: Power Electronics- 3 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Power Electronics- 3
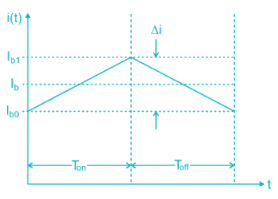
In a type A chopper, the maximum value of Ripple current is
A boost – regulator has an Input voltage 8V and the average output voltage of 24 V the duty cycle is _
A DC chopper operates on 220 V dc and frequency of 500 Hz, feeds on RL load of the output voltage of chopper is 180 V the ON time of the chopper is –(in msec)
DC chopper feed an RLE load. If the value of E increased by 20%, the current ripple
A class C chopper is operated from 230 V battery the load is a dc motor with R = 0.15 Ω, L = 12 mH and Eb = 120 V. The duty cycle of the chopper to achieve regenerative braking at the rated current of 12 ampere would be equal to
A single - quadrant chopper is operating with the following specification: Ideal battery of 240 V; on time (Ton) = 1.5 ms, OFF time = 2 ms. The Form factor factor will be –
A class C chopper is operated from a 220 V battery. The load is a dc motor with R = 0.1 Ω, L = 10 mH and Eb = 100 V. The rated current is 10 A. The duty cycle in motoring mode is
A buck converter is to be designed where Vs = 10V, Vo = 5V,R = 500Ω. The switching frequency is decided to be 20 kHz. Allowable current ripple is 5 mA. The optimum value of inductor is
A step-up chopper shown in figure is to deliver 3A
In to the 10 Ω load. The battery voltage is 12 V, L = 20 μH, C = 100 μF and chopper frequency is 50 kHz. Determine the battery current variation in ampere
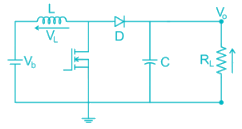
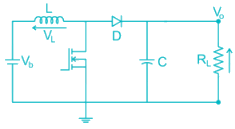
In the circuit shown below, if load R = 500 Ω, switching frequency is 25 kHz and peak to peak ripple current of inductor is limited to 0.9 A then the filter inductance L is"



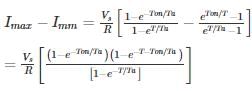

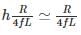
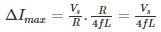
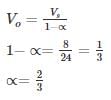

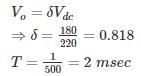
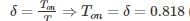 (2×10−3) = 1.636 msec
(2×10−3) = 1.636 msec