Test: Price And Output Determination- 2 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Business Economics for CA Foundation - Test: Price And Output Determination- 2
Which of the following falls under micro economics?
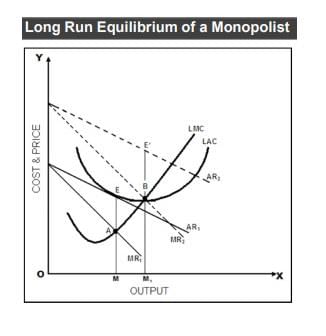
For a monopolist, the necessary condition for equilibrium is :
Who defines Economics in terms of Dynamic Growth and Development?
Under ________ market condition, firms make normal profit in the long run:
A study of how increase in the corporate income tax rate will affect the natural unemployment rate is an example of:
The Kinked demand curve model explains the market situation
Kinked demand curve hypothesis is given by:
Normative aspect of Economics is given by:
Under which market structure, average revenue of a firm is equal to its marginal revenue :
If under perfect competition, the price line lies below the average cost curve, the firm would :
Demand curve is equal to MR curve in which market?
Price discrimination is possible only when.
Which of these is the best example of oligopoly?
When elasticity of demand is Equal to one in monopoly, marginal Revenue will be _______.
The price discrimination under monopoly will be possible under which of the following conditions?
__________ type of curve is found in oligopoly.
Under perfect competition, in the long run, firms earn:
Which market have characteristic of product differentiation?
In monopoly, the demand curve facing the firm is:
In monopolistic competition, long-run equilibrium occurs when:
__________ is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply:
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of oligopoly?
|
86 videos|255 docs|58 tests
|