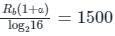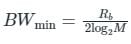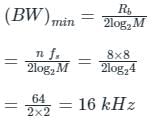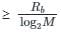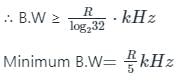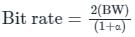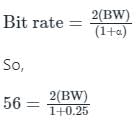Test: Pulse Shaping and Intersymbol Interference - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pulse Shaping and Intersymbol Interference
Pulse Shaping in line coding is used for
Data rate of 12 kbps is to be transmitted over a channel of bandwidth 8 kHz by using Nyquist criterion pulses. The value of the roll-off factor ‘ α’ that can be used is ______. (Correct up to 2 decimal places)
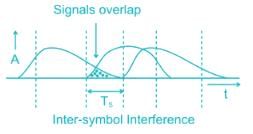
The phenomenon of overlapping of adjacent bits due to pulse spreading is:
An ideal band-pass channel 500 Hz - 2000 Hz is deployed for communication. A modem is designed to transmit bits at the rate of 4800 bits/s using 16-QAM. The roll-off factor of a pulse with a raised cosine spectrum that utilizes the entire frequency band is ________
A speech signal is sampled at 8 kHz and encoded into PCM format using 8 bits/sample. The PCM data is transmitted through a baseband channel via 4-level PAM. The minimum bandwidth (in kHz) required for transmission is ________
The bit rate of a digital communication system is R Kbits/sec. The modulation used is 32-QAM. The minimum band width for intersymbol interference free transmission is –
Consider binary data transmission at a rate of 56 kbps using baseband binary pulse amplitude modulation (PAM) that is designed to have a raised-cosine spectrum. The transmission bandwidth (in kHz) required for a roll-off factor of 0.25 is ________∙
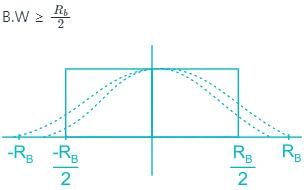
Four messages are band limited to W, W, 2W & 3W are to be multiplexed using TDM. The minimum B.W required for transmission is




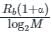 where α is called roll-off factor.
where α is called roll-off factor.