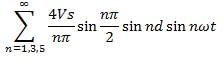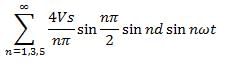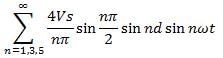Test: Pulse Width Modulation Inverter - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Pulse Width Modulation Inverter
In the single-pulse width modulation method, the output voltage waveform is symmetrical about __________
The shape of the output voltage waveform in a single PWM is
In the single-pulse width modulation method, the Fourier coefficient an is given by
In case of a single-pulse width modulation with the pulse width = 2d, the peak value of the fundamental component of voltage is given by the expression
Find the peak value of the fundamental component of voltage with a pulse width of 2d = 90 and Vs = 240 V for single-pulse modulation in a full wave bridge inverter.
In the single-pulse width modulation method, the Fourier coefficient bn is given by
In the single-pulse width modulation method, when the pulse width of 2d is equal to its maximum value of π radians, then the fundamental component of output voltage is given by
In case of a single-pulse width modulation with the pulse width = 2d, to eliminate the nth harmonic from the output voltage
In case of a single-pulse width modulation with the pulse width = 2d, to eliminate the 3rd harmonic from the output voltage waveform, the value of the pulse width (2d) must be
Which of the following pair is correct?
I. Single - pulse - width modulation control - There is only one pulse per half cycle and the width of the pulse is varied to control the inverter output voltage
II. Multiple - pulse - width modulation - The harmonic content can be reduced by using several pulses in each half - cycle of output voltage