Test: Reasoning Ability - 5 - Bank Exams MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Reasoning Ability - 5
Directions: Read both the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Give Answer:
(a) If Only conclusion I follows.
(b) If Only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If Neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Statement
Only a few Cakes are Lake
All Lake are Bake
No Bake is Fake
Conclusion
I. All Cake can be Fake
II. Some Bake is not a Cake
Directions: Read both the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Give Answer:
(a) If Only conclusion I follows.
(b) If Only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If Neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Statement
Only a few Mail are Tail
All Mail are Rail
No Rail is Nail
Conclusion
I. No Mail is Nail
II. Some Rail is not a Tail
Directions: In each of the following questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements followed by some conclusions. Find the conclusion which is definitely true.
Statements:
Q > T > V = I;
L > B > R ≥ I;
X ≤ Y ≤ L
Conclusions:
L > B > R ≥ I;
X ≤ Y ≤ L
Directions: In each of the following questions, the relationship between different elements is shown in the statements followed by some conclusions. Find the conclusion which is definitely true.
Statements:
K < B > S = I;
H = N ≥ R > X;
H ≤ L = I
Conclusions:
Directons: Read both the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Give Answer:
(a) If Only conclusion I follows.
(b) If Only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If Neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
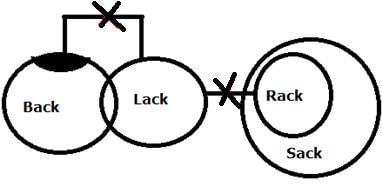
Statement
Only a few Back are Lack
No Lack is Rack
All Racks are Sack
Conclusion
I. All Back can never be Rack
II. Some Lack being Sack is a possibility
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
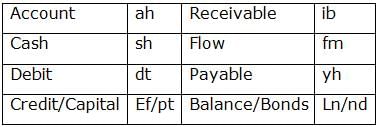
‘ Account Receivable Cash Flow ’ means ‘ ah ib sh fm’,
‘ Cash Debit Account Payable’ means ‘ sh dt ah yh’,
‘ Cash Credit Payable Capital’ means ‘ sh ef pt yh’,
‘ Balance Receivable Debit Bond’ means ‘ ln nd dt ib ’
Q. What does "ib" represent in a code language?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
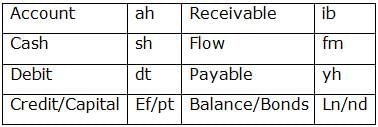
‘ Account Receivable Cash Flow ’ means ‘ ah ib sh fm’,
‘ Cash Debit Account Payable’ means ‘ sh dt ah yh’,
‘ Cash Credit Payable Capital’ means ‘ sh ef pt yh’,
‘ Balance Receivable Debit Bond’ means ‘ ln nd dt ib ’
Q. If “Balance flow” is coded as “ln fm”, then what does “nd sh ah” represent in the code language?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
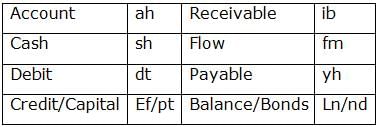
‘ Account Receivable Cash Flow ’ means ‘ ah ib sh fm’,
‘ Cash Debit Account Payable’ means ‘ sh dt ah yh’,
‘ Cash Credit Payable Capital’ means ‘ sh ef pt yh’,
‘ Balance Receivable Debit Bond’ means ‘ ln nd dt ib ’
Q. What is the code for ‘Cash Payable’ in the given language?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
In a certain code language
‘ Account Receivable Cash Flow ’ means ‘ ah ib sh fm’,
‘ Cash Debit Account Payable’ means ‘ sh dt ah yh’,
‘ Cash Credit Payable Capital’ means ‘ sh ef pt yh’,
‘ Balance Receivable Debit Bond’ means ‘ ln nd dt ib ’
Q. If “Credit Receivable” is coded as “ef ib”, What is the code for ‘Capital flow’ in the given language?
How many such pairs of letters are in the word “ CHRISTMAS” which has as many letters between them in the English alphabetical order(from both forward and backward direction)?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
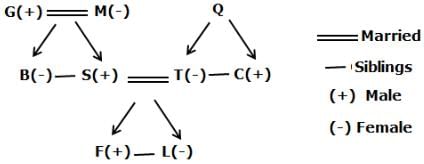
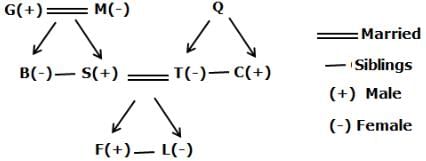
G is the father-in-law of T who is the only daughter of Q. S is the father of F who is the nephew of B. C is the brother-in-law of S. L is the daughter of T who is the daughter-in-law of M. B is the only daughter of M. B is an unmarried person in the family.
Q. Who among the following person is the spouse of S?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
G is the father-in-law of T who is the only daughter of Q. S is the father of F who is the nephew of B. C is the brother-in-law of S. L is the daughter of T who is the daughter-in-law of M. B is the only daughter of M. B is an unmarried person in the family.
Q. How C is related to T?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
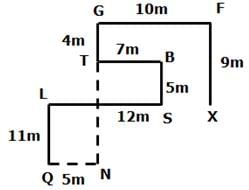
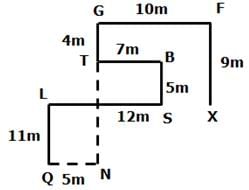
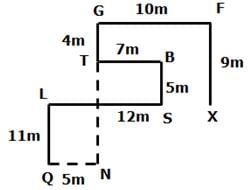
Mr Jina starts walking from point X towards the north for 9m to reach point F where he turns to the west direction and walks for 10m to reach point G where he turns to the left and walks for 4m to reach point T. Then he turns to the left and walks for 7m to reach point B where he turns to the south and walks for 5m to reach Point S. Then he turns to the right and walks for 12m to reach point L where he turns to the left and walks for 11m to reach point Q.
Q. From point Q, If Jina walks for 15m to the east and turns to the north, then which of the following point she will reach first?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Mr Jina starts walking from point X towards the north for 9m to reach point F where he turns to the west direction and walks for 10m to reach point G where he turns to the left and walks for 4m to reach point T. Then he turns to the left and walks for 7m to reach point B where he turns to the south and walks for 5m to reach Point S. Then he turns to the right and walks for 12m to reach point L where he turns to the left and walks for 11m to reach point Q.
Q. If point N is east of Point Q and south of point T, then what is the distance between T and N?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
Mr Jina starts walking from point X towards the north for 9m to reach point F where he turns to the west direction and walks for 10m to reach point G where he turns to the left and walks for 4m to reach point T. Then he turns to the left and walks for 7m to reach point B where he turns to the south and walks for 5m to reach Point S. Then he turns to the right and walks for 12m to reach point L where he turns to the left and walks for 11m to reach point Q.
Q. What is the direction of point S with respect to point X?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
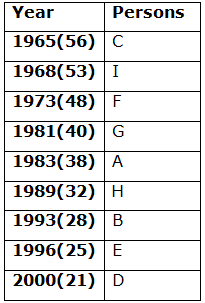
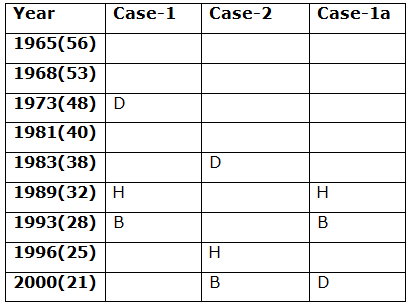
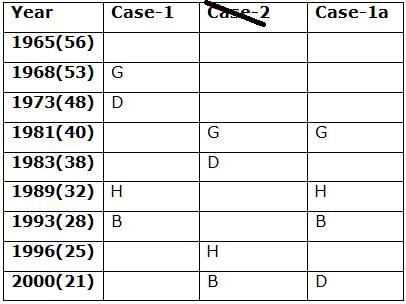
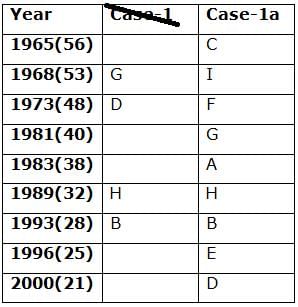
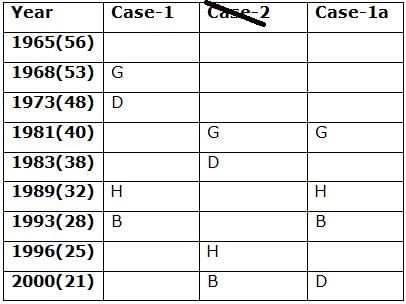
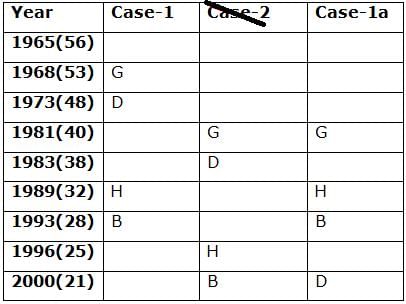
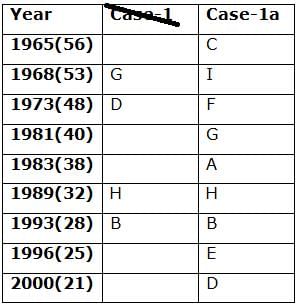
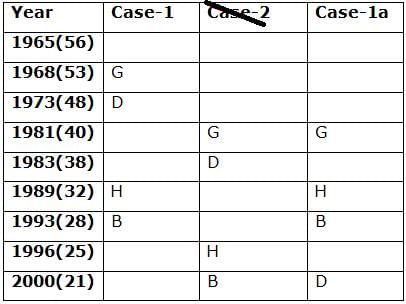
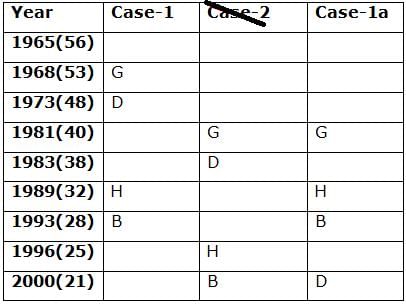
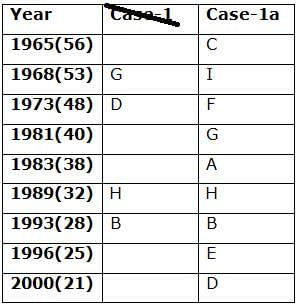
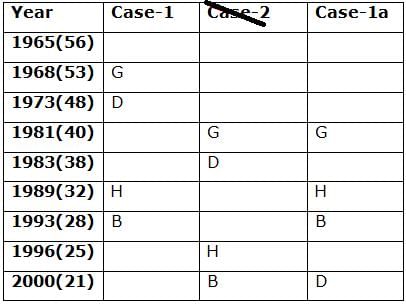
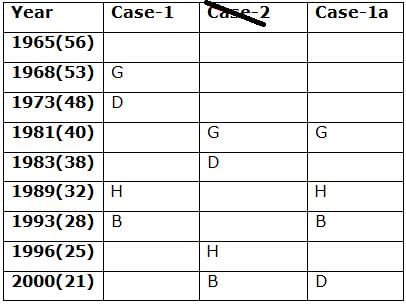
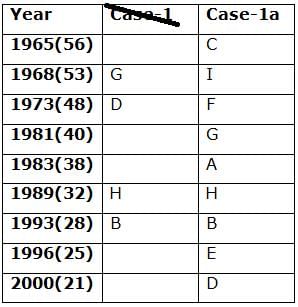
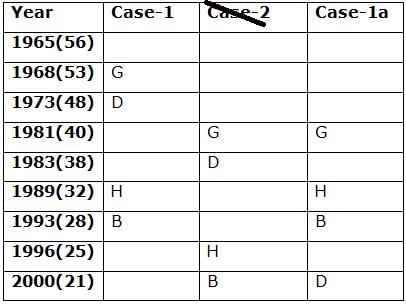
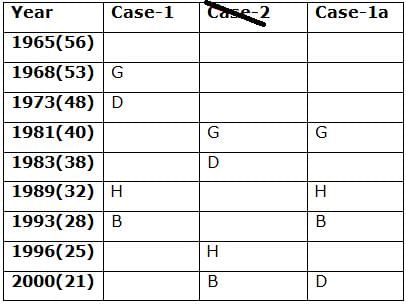
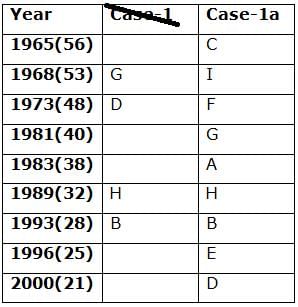
Nine persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are born in different years- 1965, 1968, 1973, 1981, 1983, 1989, 1993, 1996, and 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. Their ages are calculated with respect to the year 2021.
Only two persons are born between D and H who is four years elder than B. The number of persons born between D and B is the same as the number of persons born between H and G. The sum of the ages of H and G is more than 70. The sum of the ages of F and I is 101. The number of persons elder than I is the same as the number of persons younger than E. C is elder than A.
Q. How many persons are born between I and A?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are born in different years- 1965, 1968, 1973, 1981, 1983, 1989, 1993, 1996, and 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. Their ages are calculated with respect to the year 2021.
Only two persons are born between D and H who is four years elder than B. The number of persons born between D and B is the same as the number of persons born between H and G. The sum of the ages of H and G is more than 70. The sum of the ages of F and I is 101. The number of persons elder than I is the same as the number of persons younger than E. C is elder than A.
Q. In which of the following year does E was born?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are born in different years- 1965, 1968, 1973, 1981, 1983, 1989, 1993, 1996, and 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. Their ages are calculated with respect to the year 2021.
Only two persons are born between D and H who is four years elder than B. The number of persons born between D and B is the same as the number of persons born between H and G. The sum of the ages of H and G is more than 70. The sum of the ages of F and I is 101. The number of persons elder than I is the same as the number of persons younger than E. C is elder than A.
Q. Four of the five among the following are similar in such a way to form a group, who among the following doesn’t belong to the group?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are born in different years- 1965, 1968, 1973, 1981, 1983, 1989, 1993, 1996, and 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. Their ages are calculated with respect to the year 2021.
Only two persons are born between D and H who is four years elder than B. The number of persons born between D and B is the same as the number of persons born between H and G. The sum of the ages of H and G is more than 70. The sum of the ages of F and I is 101. The number of persons elder than I is the same as the number of persons younger than E. C is elder than A.
Q. What is the sum of the ages of B and I?
Directions: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions.
Nine persons- A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I are born in different years- 1965, 1968, 1973, 1981, 1983, 1989, 1993, 1996, and 2000 but not necessarily in the same order. Their ages are calculated with respect to the year 2021.
Only two persons are born between D and H who is four years elder than B. The number of persons born between D and B is the same as the number of persons born between H and G. The sum of the ages of H and G is more than 70. The sum of the ages of F and I is 101. The number of persons elder than I is the same as the number of persons younger than E. C is elder than A.
Q. If A’s brother was born two years after A, then what is the age of A’s brother?


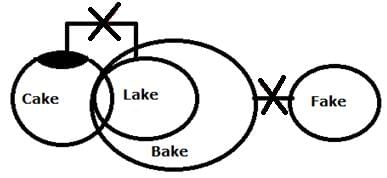
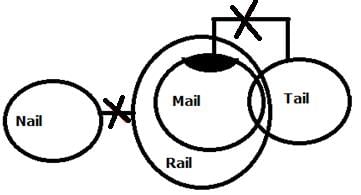

 Both conclusions I and II follow.
Both conclusions I and II follow.