Test: Rotational Motion - 2 - Grade 9 MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Rotational Motion - 2
The radius of gyration 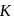 of a hollow sphere of mass
of a hollow sphere of mass 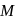 and radius
and radius 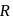 about a certain axis is equal to
about a certain axis is equal to 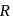 . Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.
. Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.
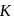 of a hollow sphere of mass
of a hollow sphere of mass 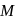 and radius
and radius 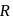 about a certain axis is equal to
about a certain axis is equal to 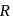 . Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.
. Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.A wheel having angular momentum 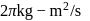 about its vertical axis, rotates at the rate of
about its vertical axis, rotates at the rate of 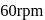 about this axis, The torque which can stop the wheel's rotation in 30 sec would be
about this axis, The torque which can stop the wheel's rotation in 30 sec would be
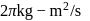 about its vertical axis, rotates at the rate of
about its vertical axis, rotates at the rate of 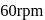 about this axis, The torque which can stop the wheel's rotation in 30 sec would be
about this axis, The torque which can stop the wheel's rotation in 30 sec would beA force 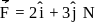 is applied to an object that is pivoted about a fixed axle aligned along the z-coordinate axis. If the force is applied at the point
is applied to an object that is pivoted about a fixed axle aligned along the z-coordinate axis. If the force is applied at the point 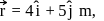 then the magnitude of the net torque about the z-axis is
then the magnitude of the net torque about the z-axis is
 . If radius of the ball be
. If radius of the ball be  , then the fraction of total energy associated with its rotational energy will be
, then the fraction of total energy associated with its rotational energy will be
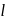 is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis through
is free to rotate in a vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis through 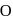 . The rod begins rotating from rest from its unstable equilibrium position. When it has turned through an angle
. The rod begins rotating from rest from its unstable equilibrium position. When it has turned through an angle 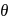 , its angular velocity
, its angular velocity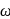 is given as
is given as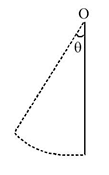
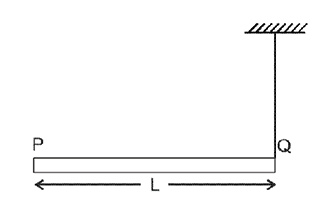
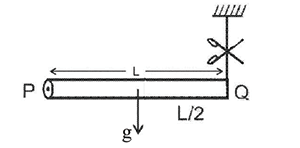
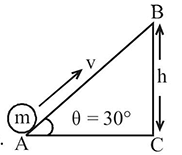
A rod  of mass
of mass  and length
and length  is hinged
is hinged 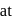 end P. The rod is kept horizontal by a massless string tied to point
end P. The rod is kept horizontal by a massless string tied to point 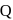 as shown in figure. When string is cut, the initial angular acceleration of the rod is
as shown in figure. When string is cut, the initial angular acceleration of the rod is
 rolls on a smooth horizontal surface at
rolls on a smooth horizontal surface at 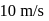 . It then rolls up a smooth inclined plane of inclination
. It then rolls up a smooth inclined plane of inclination 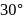 with the horizontal. Then what is the height (in meter) attained by the sphere before it stops ?
with the horizontal. Then what is the height (in meter) attained by the sphere before it stops ?
 wheel
wheel 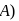 is attached by non-stretching belt to a wheel of radius
is attached by non-stretching belt to a wheel of radius 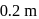 (wheel
(wheel 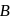 ). The belt does not slip. By the time wheel
). The belt does not slip. By the time wheel 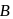 turns through 1 revolution, wheel
turns through 1 revolution, wheel 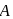 will rotate through
will rotate through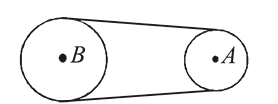
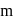 and radius
and radius 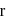 are arranged as shown in the figure. If
are arranged as shown in the figure. If 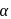 is the angular acceleration of the lower disc and
is the angular acceleration of the lower disc and 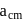 is acceleration of centre of mass of the lower disc, then relation between
is acceleration of centre of mass of the lower disc, then relation between 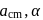 and
and 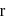 is
is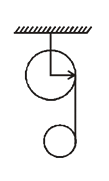
A wheel of radius 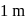 rolls forward half a revolution on a horizontal ground. The magnitude of the displacement of the point of the wheel initially in contact with the ground is
rolls forward half a revolution on a horizontal ground. The magnitude of the displacement of the point of the wheel initially in contact with the ground is
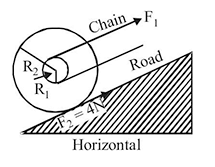
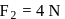 . With what force
. With what force 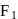 (in newton) must the chain pull on Horizontal
(in newton) must the chain pull on Horizontalthe sprocket wheel if
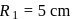 and
and 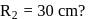
The radius of gyration 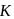 of a hollow sphere of mass
of a hollow sphere of mass 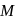 and radius
and radius 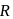 about a certain axis is equal to
about a certain axis is equal to 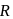 . Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.
. Find the distance of that axis from the centre of the sphere.
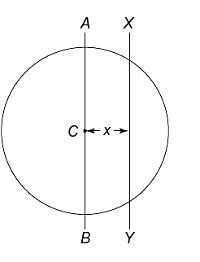
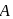 and
and 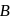 are moving in circular orbits with angular velocity
are moving in circular orbits with angular velocity 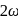 and
and 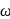 respectively. Their positions are as shown at
respectively. Their positions are as shown at 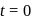 . Find the time when they will meet for the first time.
. Find the time when they will meet for the first time.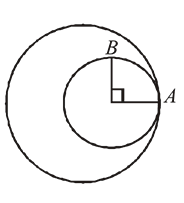



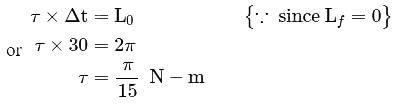

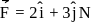
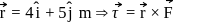
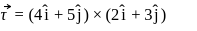
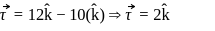
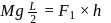
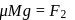
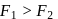
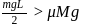 or
or 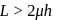
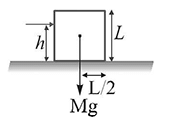
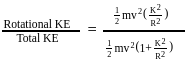
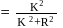
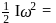 Loss of potential energy
Loss of potential energy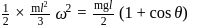
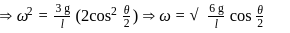
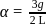
 is the radius of gyration. So from law of conservation of energy,
is the radius of gyration. So from law of conservation of energy,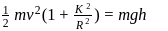
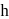 is the height attained by the sphere.
is the height attained by the sphere.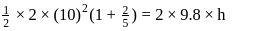 .
.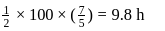
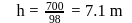
 Angular speeds of wheels
Angular speeds of wheels 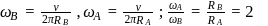
 Tr
Tr 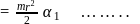
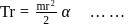
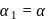
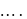
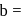 acceleration of point a
acceleration of point a 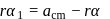
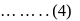
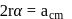
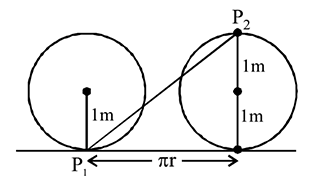
 Point
Point  after half revolution reaches at
after half revolution reaches at  vertically
vertically 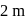 above the ground.
above the ground. Displacement
Displacement 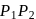
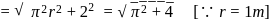
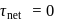
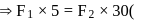 given
given 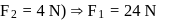
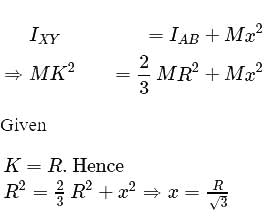
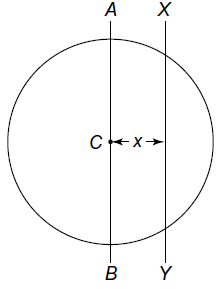
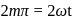
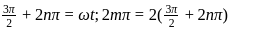
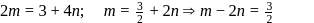
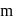 and
and 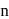 being integer. Case
being integer. Case 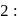 When they rotate in opposite sense
When they rotate in opposite sense 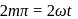
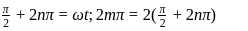
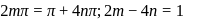
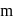 and
and 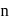 integer.
integer.















