Test: S-R Flip Flop - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: S-R Flip Flop
If the counter has 3 flip-flops, then the maximum binary number that it counts is equal to:
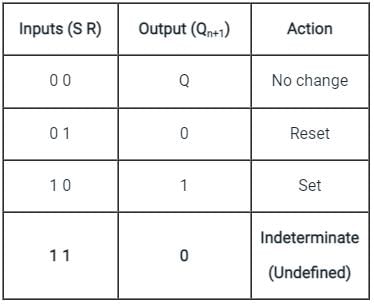
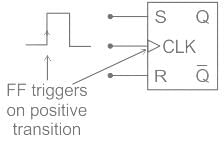
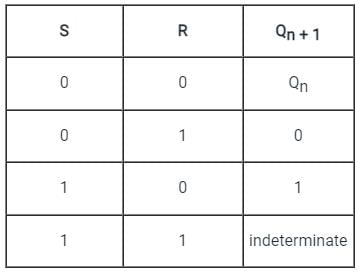
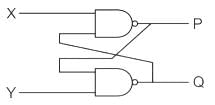
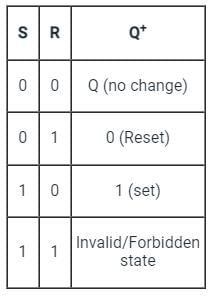
In which of the following condition the SR flip flop are unstable?
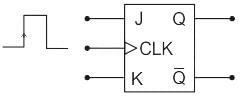
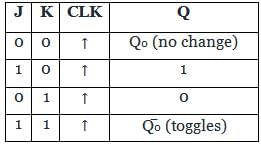
A feature that distinguishes the JK flip flop from the SR flip flop is the
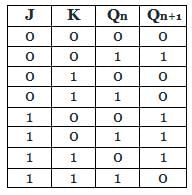
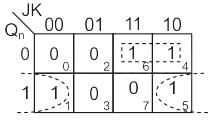
The correct combination of characteristic equation Qn + 1 of S-R flipflop and J-K flipflop respectively is
The present state of the output of an SR flip flop is HIGH. If both its inputs become LOW, what would be the new state of the output?
How many flip-flops are required to build a binary counter circuit to count from 0 to 1023 ?
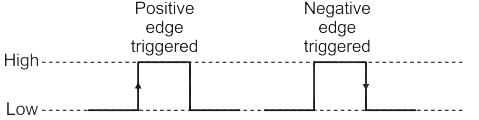
A negative edge triggered flip flop transfers data from input to output on the:
The circuits of NOR based S-R latch classified as asynchronous sequential circuits, why?
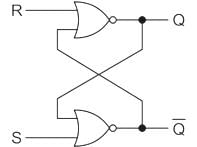
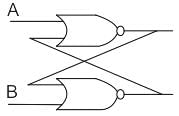
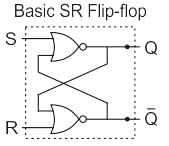
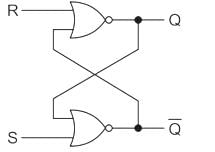
A basic S-R flip-flop can be constructed by cross-coupling of which basic logic gates?