Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 3 - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - 3
Which statement is correct for apomixis?
In the process of pollen grain development, what is the sequence of events that leads to the formation of two male gametes in angiosperms?
Which of the following statements is false?
Germ pore/germinal furrow present on the surface of pollen grain represents
Male gametophyte in angiosperms produces
Which of the following options is correct?
1. Pollination gives the guarantee of the promotion of post-pollination events that lead to fertilization
2. The events – “from pollen deposition on stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovule" are together referred to as pollen-pistil interaction
3. Pollen-pistil interaction is a dynamic process involving pollen recognition followed by only promotion (not rejection) of the pollen
4. Pistil has no ability to recognize the pollen, whether right or wrong type
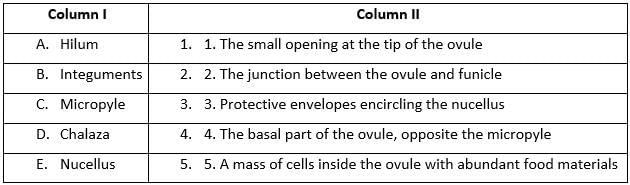
Match the following descriptions with the correct terms related to the ovule:
Pollen tablets are available in the market for:
Endosperm is completely consumed by the developing embryo in
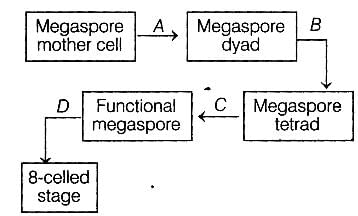
Identify the type of cell division A to D in the following flowchart.
During microsporogenesis, meiosis occurs in
Viability of pollen grains depends on
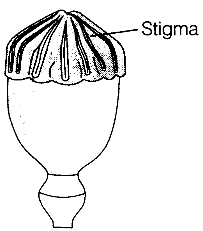
Identify the type of pistil in the diagram.
Identify the correct statement ?
- Pollination by water is quite rare in flowering plants
- All aquatic plants use water for pollination
- In most of the water-pollinated species, pollen grains are protected from wetting by a mucilaginous covering
- Plants such as Water Hyacinth and Water Lily are pollinated by water .
Which of the following statements is true regarding the characteristics and development of seeds in angiosperms?
1. Non-albuminous seeds have no residual endosperm because it is completely consumed during embryo development, while albuminous seeds retain part of the endosperm.
2. The perisperm is a type of endosperm found in seeds such as wheat and maize.
3. The cotyledons in seeds are generally thin and not swollen because they do not store significant food reserves.
4. The micropyle in the seed coat facilitates the exit of water from the seed during germination.
|
78 videos|280 docs|174 tests
|




















