Test: Soil Mechanics- 7 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Soil Mechanics- 7
Which of the following assumptions is wrongly stated in regard to Rankine’s theory of earth pressure?
A retaining wall of height H with smooth vertical backface supports a backfill inclined at an angle β with the horizontal. The backfill consists of cohesionless soil having an angle of internal friction ϕ. If the active lateral thrust acting on the wall is Pa, which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Consider the following statements:
1. Method of slices overestimates the value of factor of safety.
2. The exact value of factor of safety is obtained in ϕT = 0 analysis.
3. Reduction in shearing resistance in embankment is caused by tension crack at the top of it.
4. The plane surface of failure never occurs in saturated soils.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
What is active earth pressure at the bottom of a vertical cut, 4.0 m deep in soil with ϕ’ = 30° and c’ = 20 kN/m2 and γ = 25 kN/m3?
A 5m high vertical earth retaining wall having smooth vertical back retains non-cohesive soil with angle of internal friction 35° and unit weight γ = 18 kN/m3. If the wall is free to field and the water table is at a depth of 2m below the top of the wall, then the total horizontal active thrust (kN) per unit length acting on the wall will be
Take γsat = 20 kN/m3, γω = 10kN/m3.
A cutting is to be made in clay having cohesion 50 kPa and unit weight 22 kN/m3. If the maximum depth of cut is limited to 8.30m, determine the stability Factor against the factor of safety w.r.t. cohesion equal to 2.
A granular soil has a saturated unit weight of 20 kN/m3 and an effective angle of shearing resistance of 30°. The unit weight of water is 9.81 kN/m3. A slope is to be made on this soil deposit in which the seepage occurs parallel to the slope up to the free surface. Under this seepage condition for a factor of safety of 1.5, the safe slope angle (in degree, round off to 1 decimal place) would be ______.
A saturated sand sample has dry unit weight of 18kN/m3 and a specific gravity of 2.65. If Ɣw = 10 kN/m3, the water content of the soil is _____ .
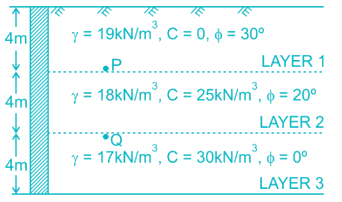
Three soil profile is used as backfill behind a smooth vertical retaining wall as shown in the figure below. The ratio of total active earth pressure (kN/m2) at Point P to Point Q will be _____ (up to two decimal places)
A 5 m high retaining wall is as shown in figure determine ranking active earth pressure (in kN/m) per unit length of the retaining wall after the formation of tension crack:( answer up to 1 decimal point)





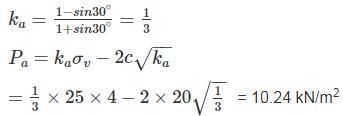

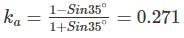



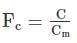





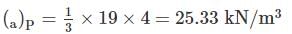 Active earth Pressure at Point Q is
Active earth Pressure at Point Q is