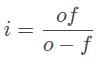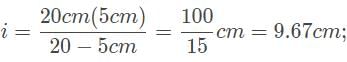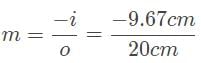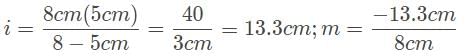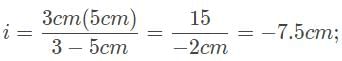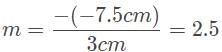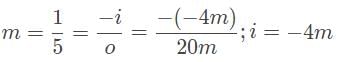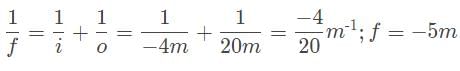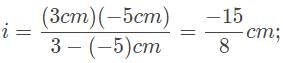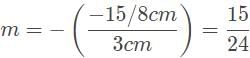Test: Spherical Mirrors - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Spherical Mirrors
Which of the following correctly describes the image produced by a plane mirror?
A student who is standing 0.5 meters from a plane mirror moves at a velocity of 0.75 meters per second for 3 seconds away from the mirror. How much further is the student from her image than when she first started moving?
Which of the following statements most accurately describes virtual image formation?
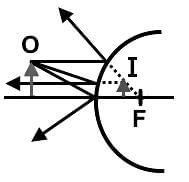
Which of the following images can be formed by a concave mirror?
I. real, inverted, and enlarged
II. virtual, upright, and enlarged
III. real, upright, and reduced
IV. virtual, inverted, and enlarged
We have our first experience with rearview mirrors when first learning to drive. Which of the following statements most accurately describes rearview mirrors?
A car drives by approximately 20 meters from the convex side of a reflective sculpture, and its image appears to be one-fifth the size of the car. What is the focal length of this reflective surface?
Which of the following would be an example of using a convex mirror effectively?
Which of the following statements correctly identifies a rule for drawing ray diagrams with mirrors?
A clown is standing in front of a fun mirror. The top half of the mirror is concave, and the bottom half of the mirror is convex. What happens to his image as the clown moves towards the mirror?
Which of the following statements best describes the causes and solutions for optical system aberrations?